🏠 Welcome to the Teemant Dashboard
The Teemant Home Dashboard offers a high-level overview of AI agent activity within the current workspace. It is designed to help managers and bot designers monitor usage and performance of deployed applications in real-time.
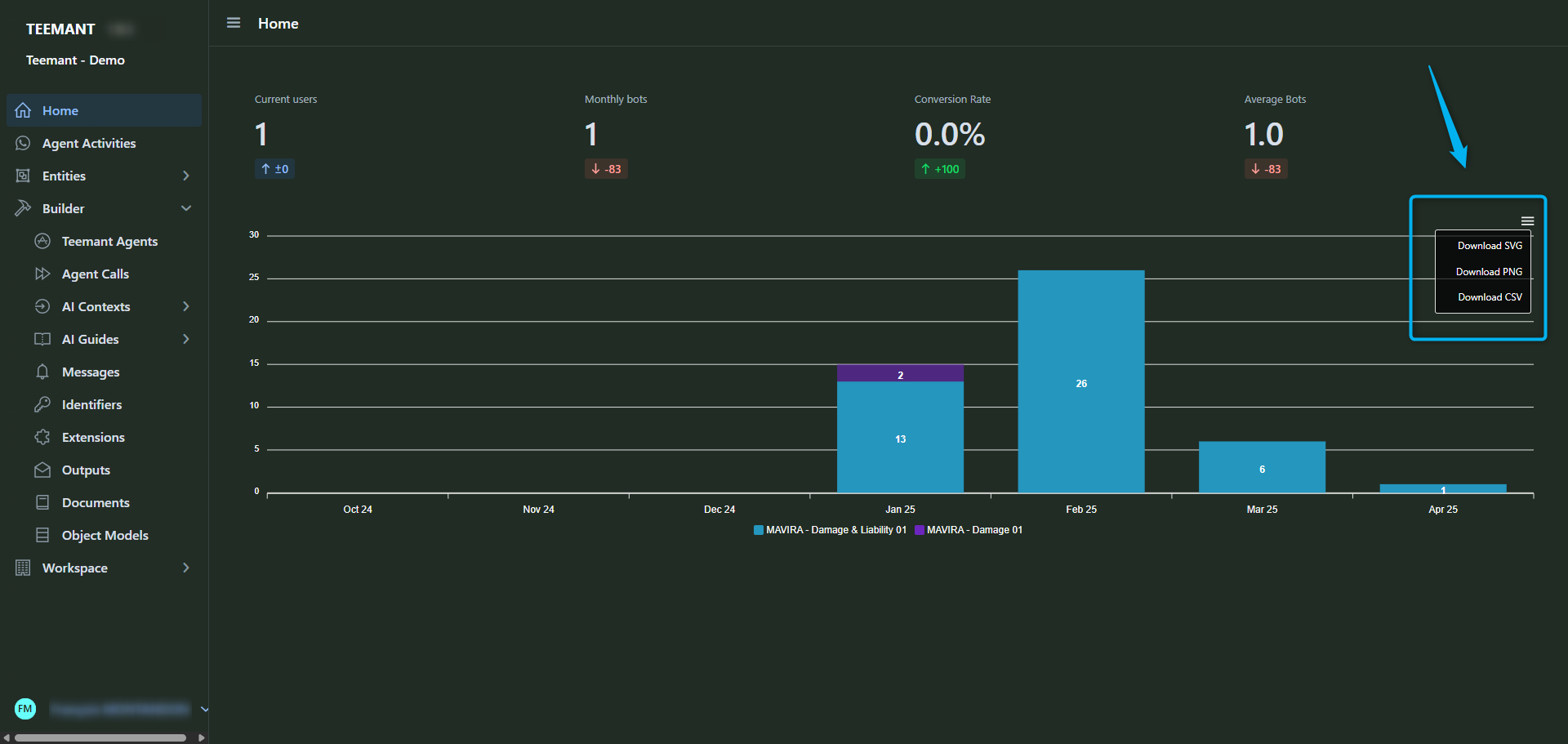
📊 Dashboard Indicators
- Current Users: Number of bot users currently interacting with an AI agent.
- Monthly Bots: Total bots triggered within the current month.
- Conversion Rate: Percentage of conversations that reached the defined success criteria (e.g., completed process).
- Average Bots: Average number of bots triggered monthly.
The bar chart below displays monthly bot activity per application, with color-coded segmentation for each Teemant App (e.g., MAVIRA - Damage 01, MAVIRA - Damage & Liability 01). This helps identify usage trends and engagement by application.
📚 Left Menu Overview
The left-side navigation menu allows structured access to all Teemant features:
- Home: Returns to the dashboard overview.
- Agent Activities: View detailed logs of all conversations between users and AI agents.
- Entities: Access structured reference data used during workflows (e.g., store lists, vehicle IDs).
- Builder: Core area for creating and configuring the AI environment:
- Teemant Agents: Configure agent personalities and capabilities.
- Agent Calls: Define logic for actions and flows triggered by agents.
- AI Contexts: Set the knowledge and instructions used by the agents.
- AI Guides: Build operational instructions (e.g., Data Collection, Checklist, etc).
- Messages: Define dynamic or static messages used in interactions.
- Identifiers: Create unique user references (like claim numbers).
- Extensions: Integrate external APIs or services.
- Outputs: Manage how data is returned or transferred after agent interaction.
- Documents: Templates for generating structured output (e.g., PDF forms).
- Object Models: Define the structure for entities used in apps.
- Workspace: Configure access rights, members, bot users, and workspace properties.
Each section is designed to be modular and intuitive, enabling seamless collaboration between AI designers, developers, and business users.
Agent Activities
Agent Activities in TeemantSoft provide a detailed record of all interactions between Teemant AI agents (such as Gemma) and bot users. This section allows bot designers and administrators to review past conversations, analyze interactions, and export data for reporting or auditing purposes.
Viewing Agent Activities
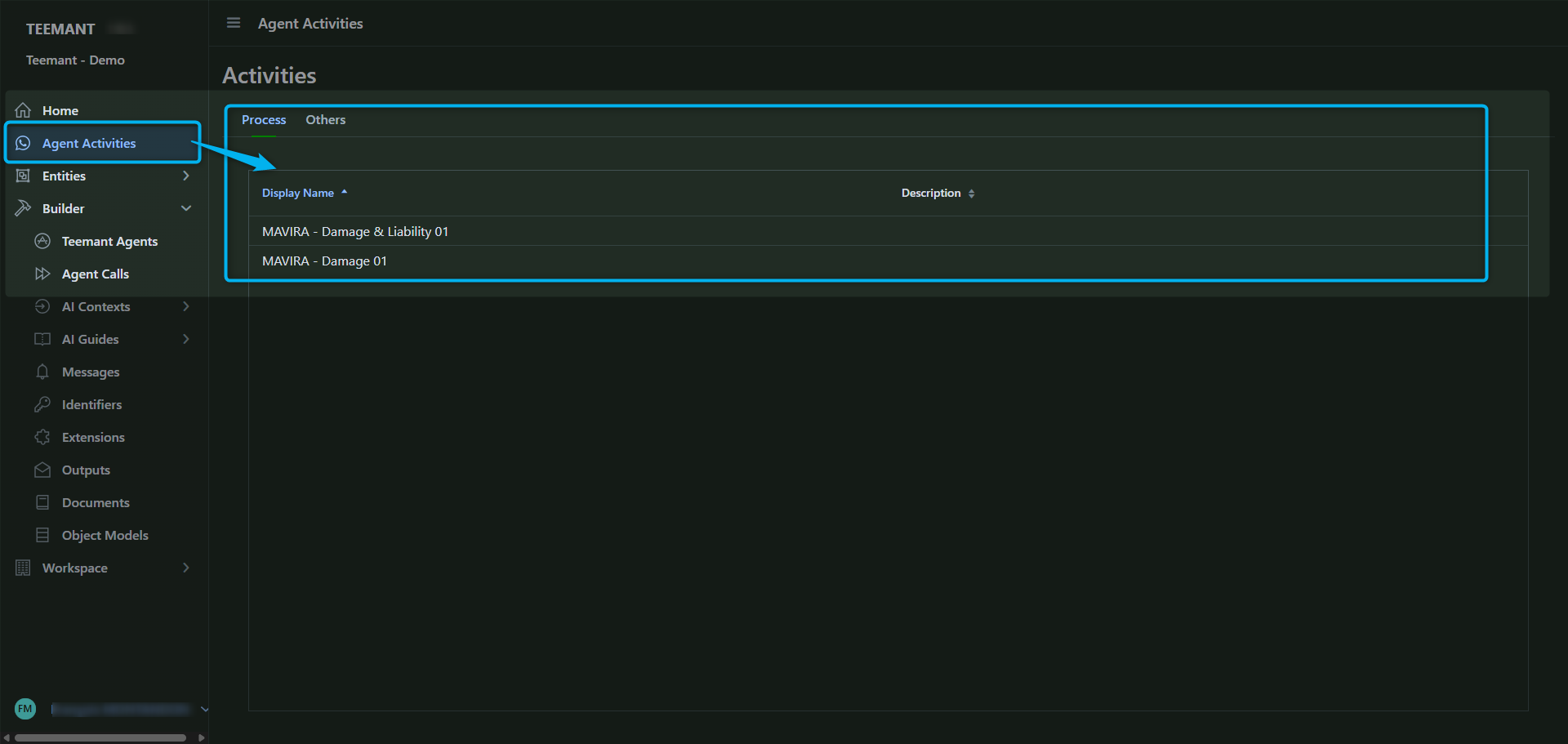
📌 How to Access:
- Navigate to Bot Activities from the left-hand menu.
- A list of recorded conversations and activities appears, displaying session names and details.
💡 Purpose:
- Helps track how AI agents interact with users.
- Provides insight into conversation flow, decision-making, and outcomes.
- Enables teams to troubleshoot and improve AI interactions.
Reviewing Interaction History
📌 Details Available for Each Activity:
- Start and End Time of the conversation.
- Reason for Termination (e.g., user-ended, timeout, or system-cancelled).
- User Identification (phone number, email, or internal identifier).
💡 Use Case: - Reviewing past interactions to understand user behavior.
- Identifying points where users dropped off or required clarification.
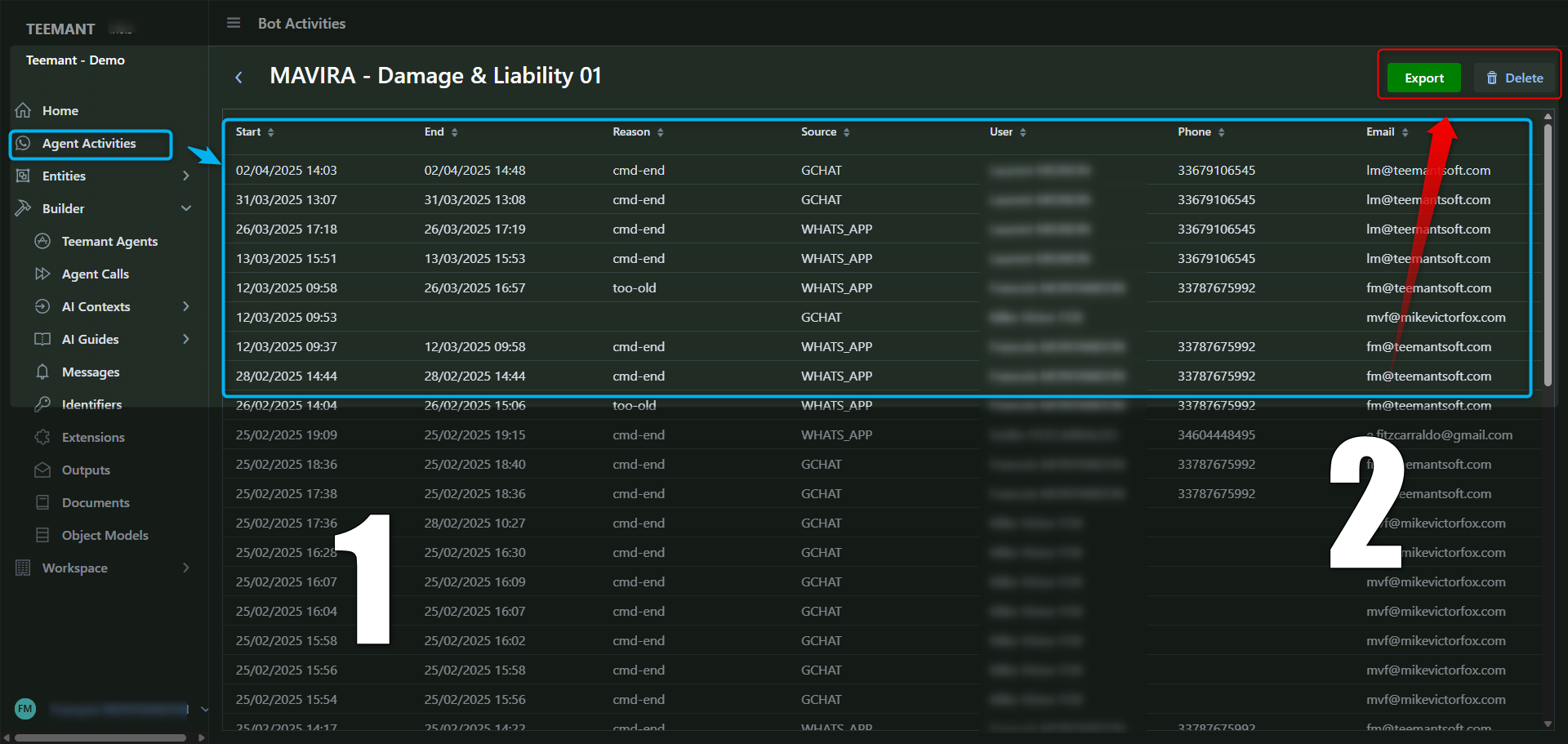
📌 Options Available in the Bot Activities Panel:
- Export: Download activity logs for external analysis or reporting.
- Delete: Remove unwanted or outdated records.
💡 Best Practices:
- Regularly export data for insights into bot performance.
- Delete irrelevant records to keep the system optimized.
Analyzing a Specific Conversation (AI Agent Instance View)
📌 Key Features:
- Displays full conversation threads between the AI agent and the bot user.
- Highlights user responses, AI agent questions, and decision points.
- Provides contextual data, including user inputs, choices, and document submissions.
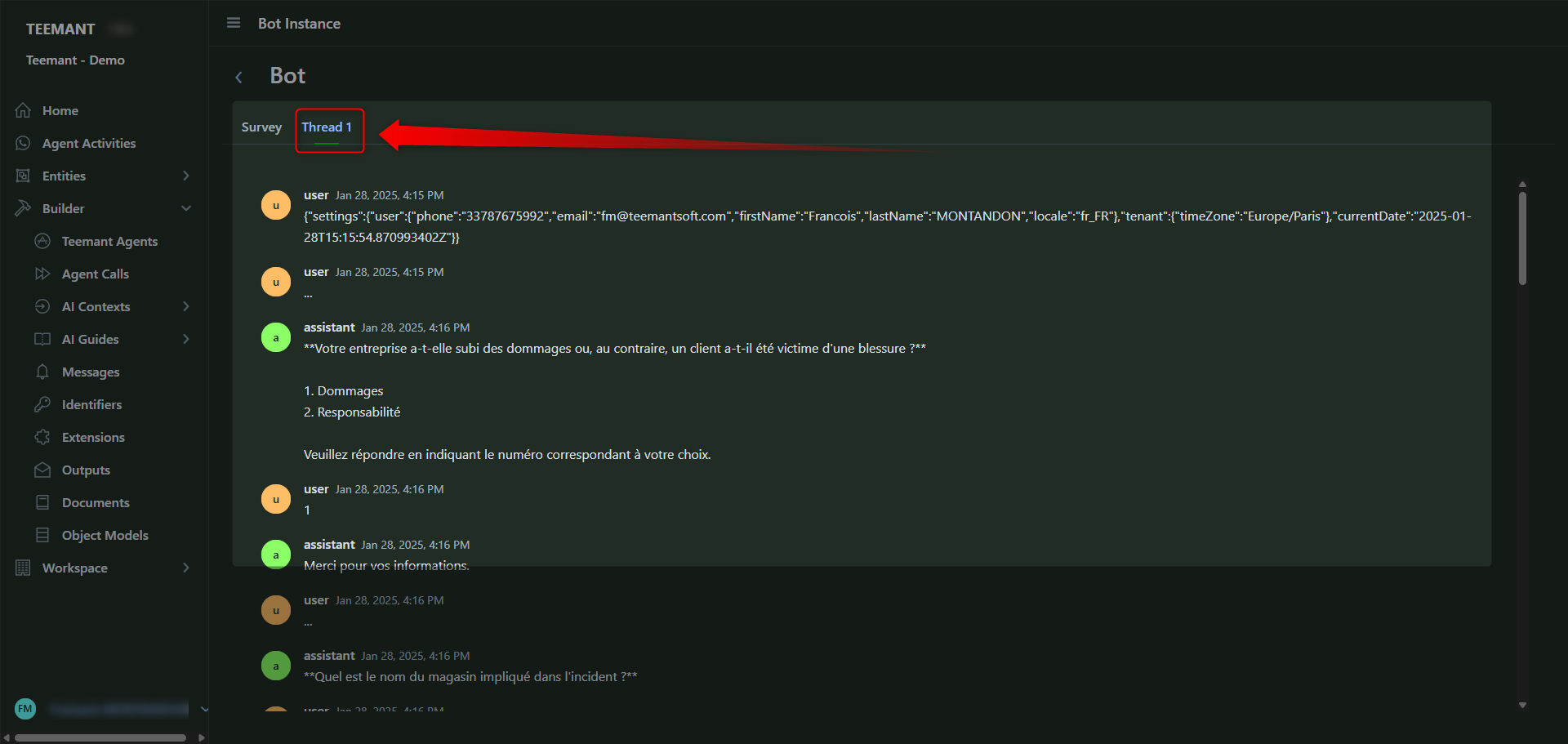
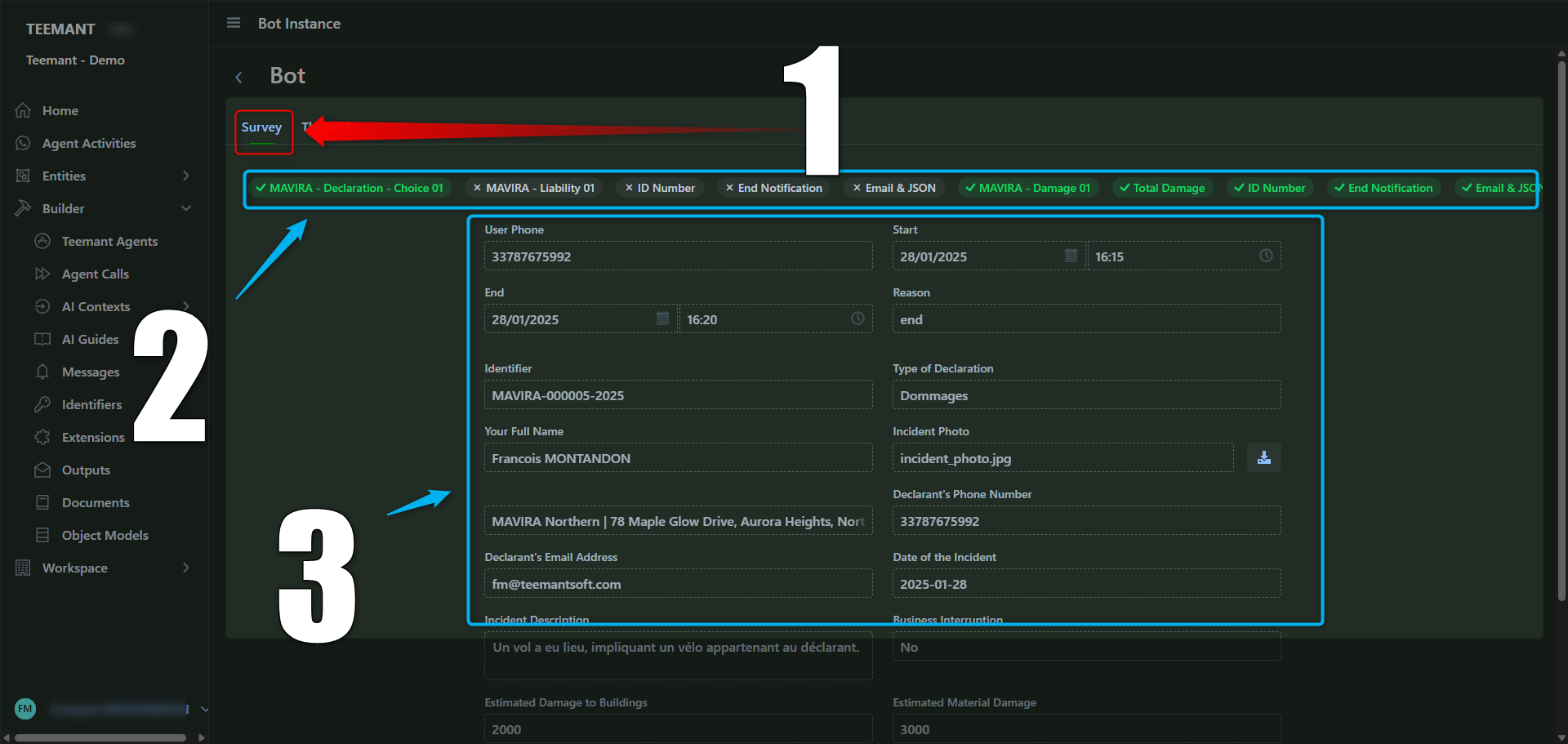
💡 Use Case:
- Troubleshooting a user complaint by analyzing their exact conversation history.
- Understanding how AI agents handle specific scenarios.
Entities and Object Models
Entities and object models are essential components of TeemantSoft's autonomous data management. They allow AI agents to access structured data, reducing reliance on external databases while maintaining the flexibility to integrate with them when needed.
What Are Entities?
Entities function as master data repositories that AI agents can reference during processes. They store structured information that can be used dynamically across applications.
📌 Examples of Entities:
- Lists of locations (e.g., store addresses, warehouses).
- Vehicle registrations (e.g., company fleet information).
- People’s IDs (e.g., employee records, customer identification numbers).
These entities can be manually created, populated from external systems, or maintained autonomously within TeemantSoft.
Creating and Managing Entities
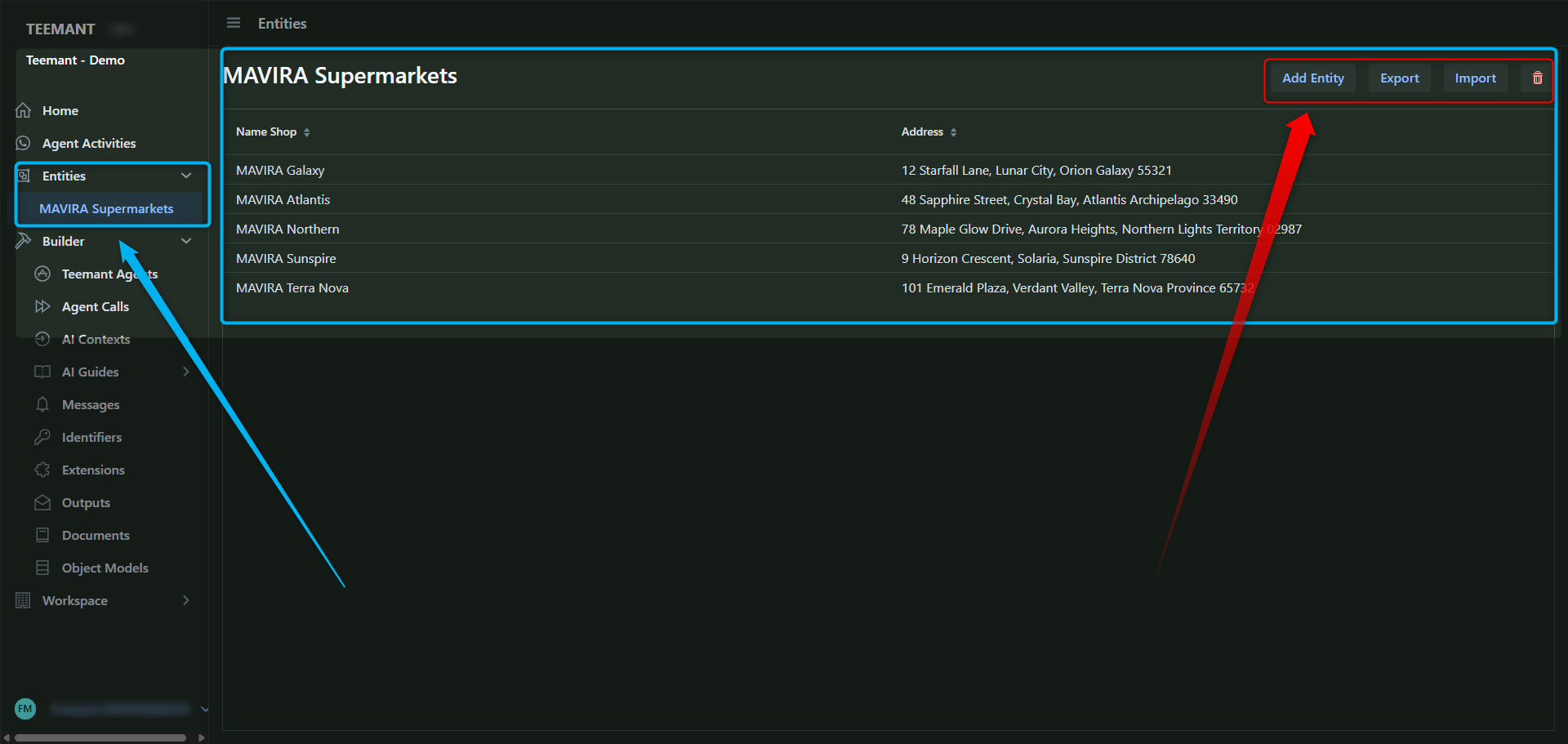
Step 1: Access the Entities Section
- Navigate to Entities in the left-hand menu.
- Select an existing entity or click "Add Entity" to create a new one.
Step 2: Populate and Manage Entity Data
Once you're inside an entity:
- Manually add data by clicking the Add Entity button (highlighted in red in the screenshot).
- Each record includes fields such as name, address, ID, etc.
- Click Export to download the dataset in CSV format.
- Use Import to upload a new batch of data.
- Click the trash bin icon to delete the entity (with caution—this action is irreversible).
💡 Use Case: A company managing multiple store locations can maintain an entity called “Company Locations”, which contains all store addresses for AI-driven queries.
Step 3: Automating Entity Population
Teemant can autonomously populate entity data based on external systems or workflow triggers. This eliminates the need for repeated manual updates and ensures data remains up-to-date.
To configure automation:
- Go to Workspace > Settings.
- Navigate to the Tasks tab.
Set up automation tasks for importing from external APIs, scheduled updates, or internal workflows.
This makes entities a powerful standalone knowledge source, even if disconnected from external databases.
More details are provided in the user manual under
Tasks
Object Models: Structuring Data in TeemantSoft
Object models define the structure of an entity, including field names, data types, and mandatory requirements.
Step 1: Creating an Object Model
- Go to Object Models in the left-hand menu.
- Click "Add Model" to create a new object.
- Define the name and purpose of the object.
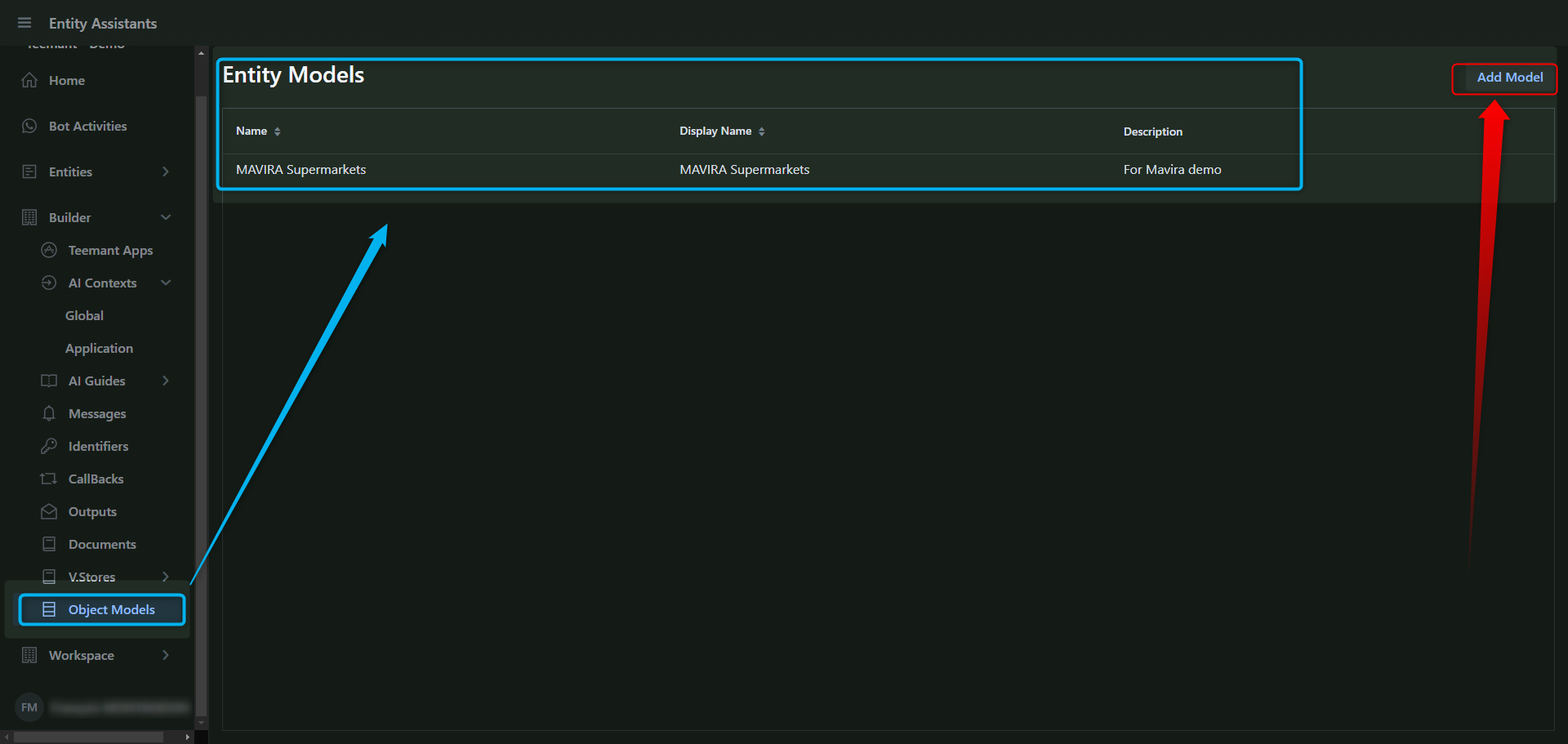
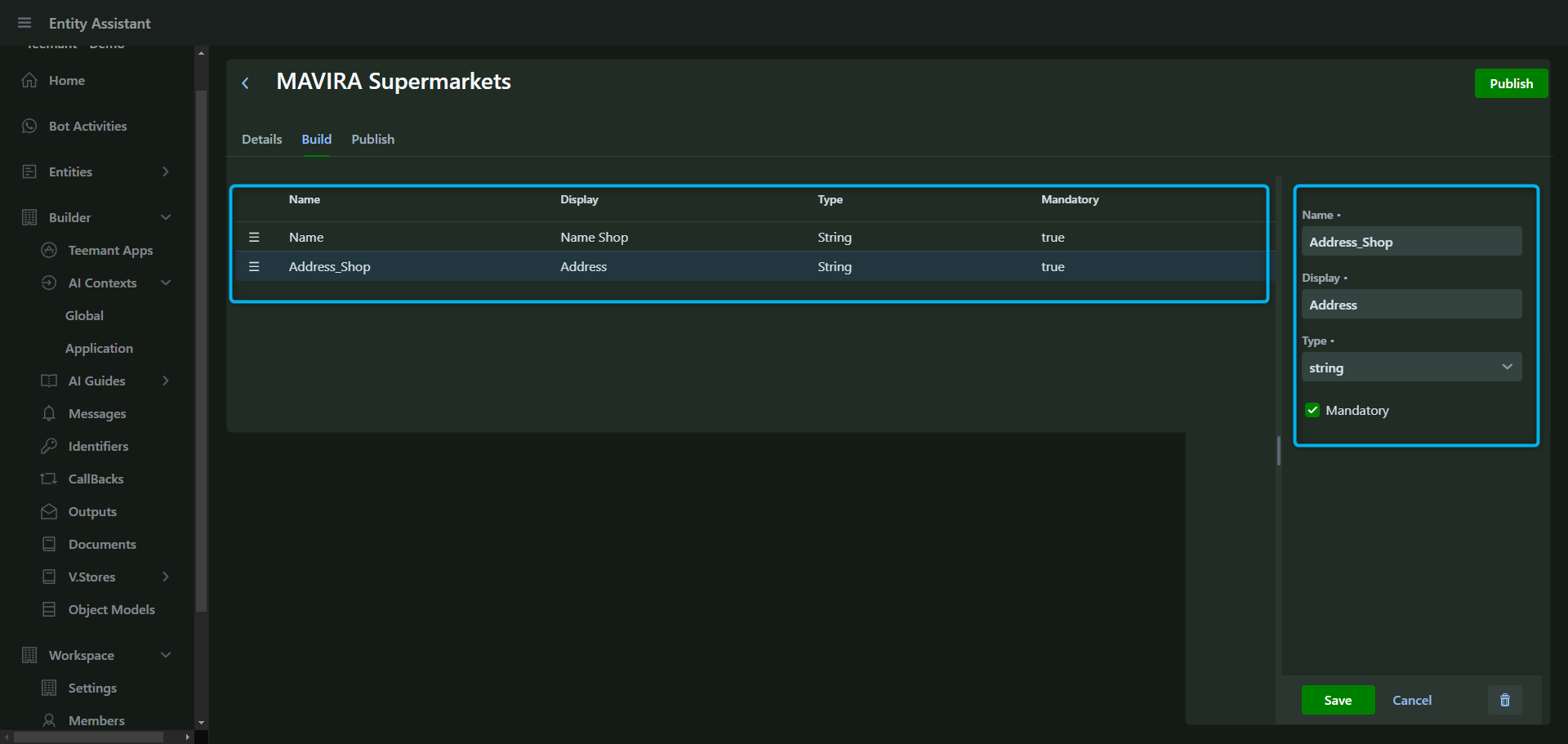
Step 2: Defining Fields
- Add field names (e.g., Name, Address, ID Number).
- Choose the data type (e.g., String, Number, Boolean).
- Mark fields as mandatory if required.
💡 Best Practice: Always plan field structures carefully, as they determine how data is stored, retrieved, and integrated with AI processes.
Publishing and Deploying Object Models
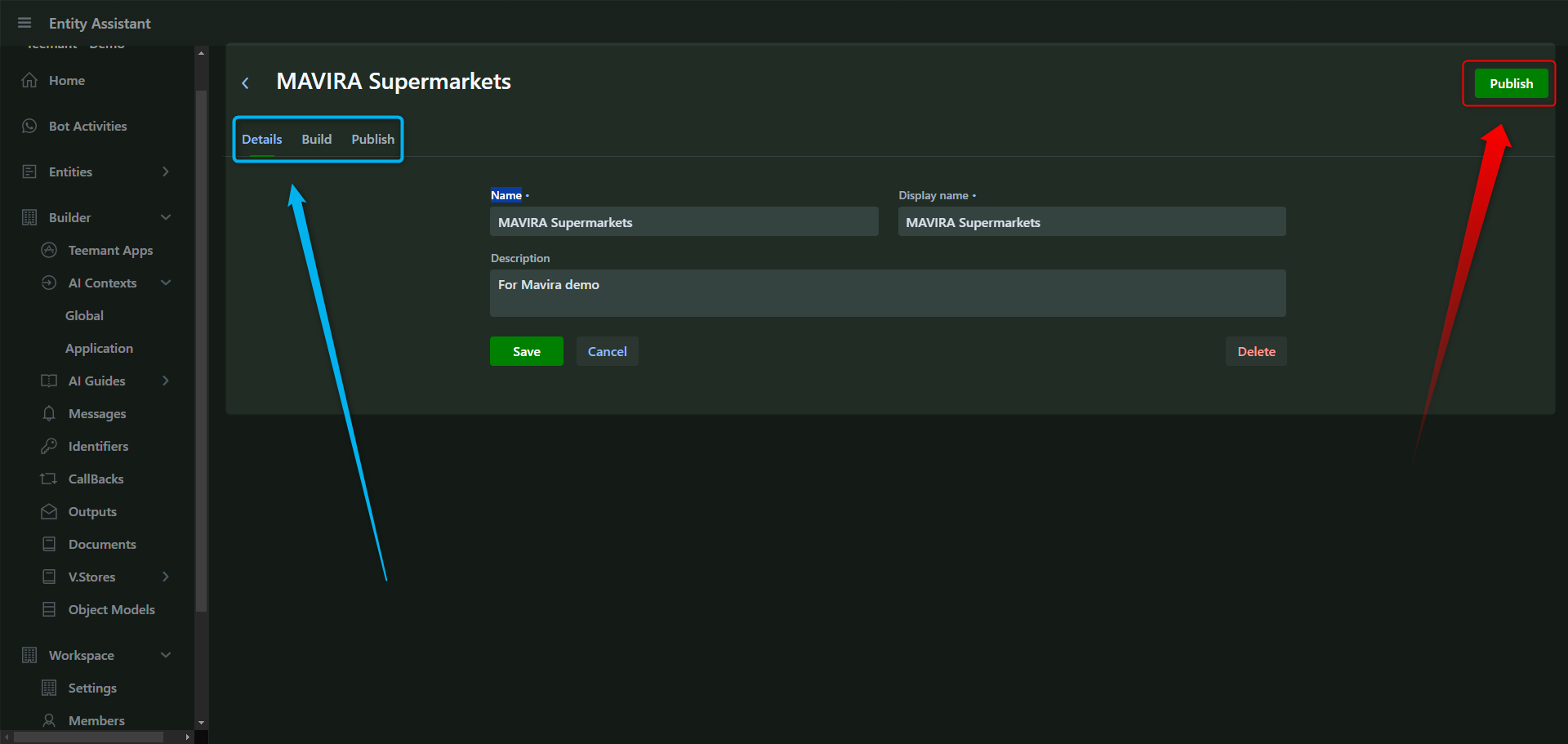
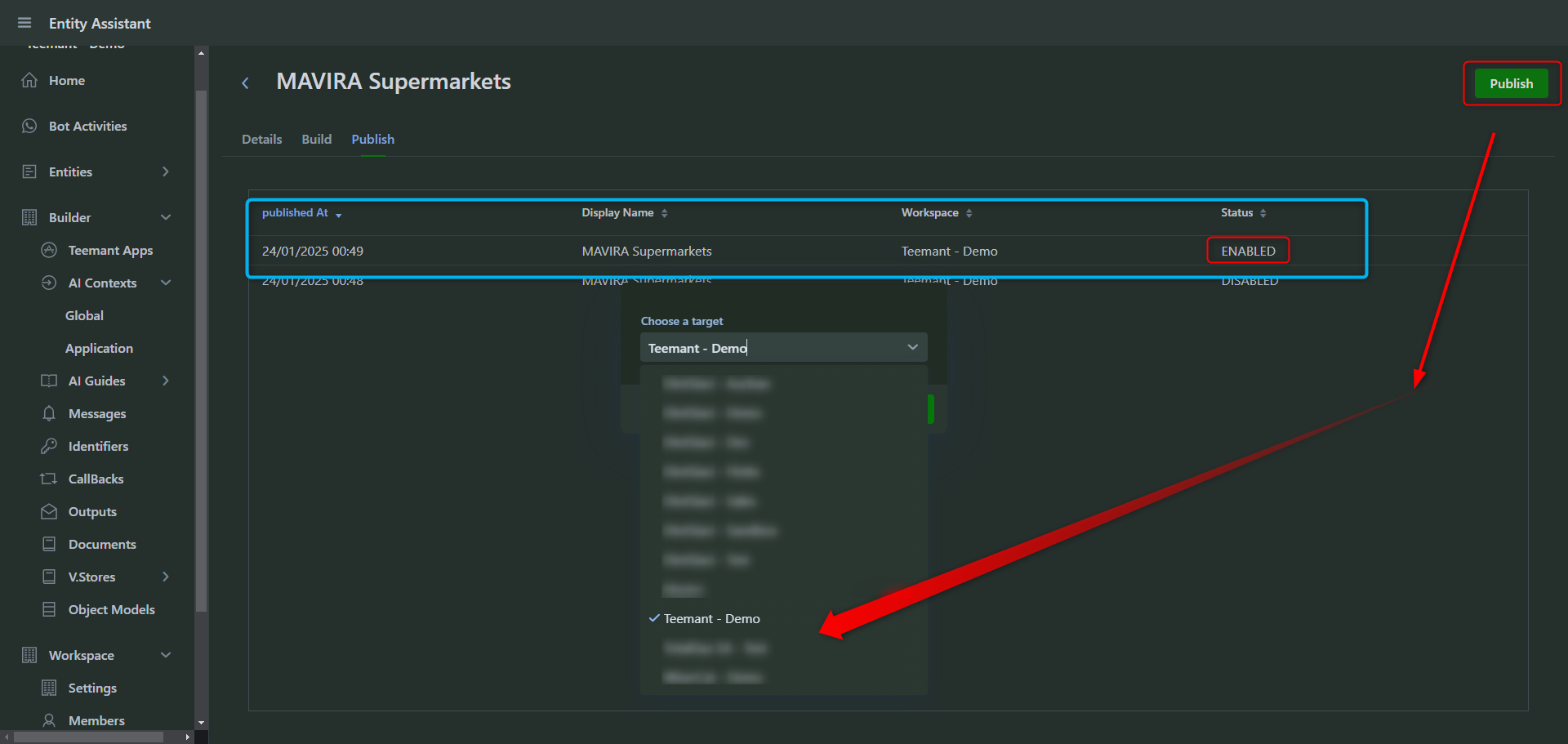
Once an object model is configured, it must be published to become available for use.
Save and Publish the Model
- Click “Save” after defining fields.
- Navigate to the Publish tab and choose the target workspace.
- Click "Publish" to deploy the model.
📌 After publishing, this object model can be used by AI agents to retrieve data during interactions.
Why This Is Powerful?
- Autonomous Database: TeemantSoft can store and manage data independently, making it fully functional without an external database.
- Integration-Ready: While it can operate standalone, it also allows external system synchronization for real-time updates.
- Scalability: AI agents can quickly retrieve structured data, improving response accuracy and efficiency in automated workflows.
🛠 Builder: Designing Intelligent Agent Workflows
Introduction
The Builder is the heart of the Teemant platform. It enables the creation of intelligent conversation flows for Teemant AI agents like Gemma, using a visual, logic-driven structure. Bot designers use this area to assemble and sequence actions—ranging from asking questions, calculating values, collecting structured data, and delivering outputs.
While Gemma executes these flows, Flint is the AI assistant that supports the bot designer in creating and refining them. You can ask Flint for help in building or debugging guides, especially within AI Guide components.
📚 What’s Inside the Builder?
AI Guides
These are the functional blocks that define what the agent will do at each step. Different guide types include:
- Data Collection – Ask structured questions and collect precise inputs.
- Checklist – Verify whether a sequence of conditions is met.
- Calculated Fields – Perform real-time calculations.
- Troubleshooting – Diagnose a situation through dynamic questioning.
- Document Questions – Help extract answers based on uploaded documents.
Each guide is created independently and added to the builder where it fits the logic.
Messages
Messages are used to deliver static or dynamic information to the user, such as:
- Informing the user about next steps.
- Providing instructions or context.
- Confirming receipt of answers.
Messages are not interactive—they’re just communication blocks triggered at specific points.
Identifiers
An Identifier is a system-generated, unique reference number used to track a specific conversation or thread. It's not meant for collecting user data (like a phone number or policy number), but rather to:
- Help the user follow up or reference their interaction later.
- Allow admins to retrieve past conversations using that reference (e.g.,
MAVIRA-000053-2025).
These are especially important in formal workflows like insurance claims or support tickets.
Extensions
Outputs are the final actions of the flow. They may include:
- Sending an email confirmation.
- Pushing structured data (e.g., JSON) to an external system.
- Creating tickets or reports.
You can combine multiple outputs at the end of a flow depending on business needs.
Teemant Agents
Teemant Agents are at the core of how virtual assistants like Gemma interact with users.
A Teemant Agent represents a complete conversation flow, made of structured blocks of logic, guides, actions, and conditions. These flows define what the AI will say and do at each step of an interaction – from greeting the user, collecting data, guiding through steps, checking rules, and triggering outputs like emails or data exports.
✍️ Interacting with the Flow
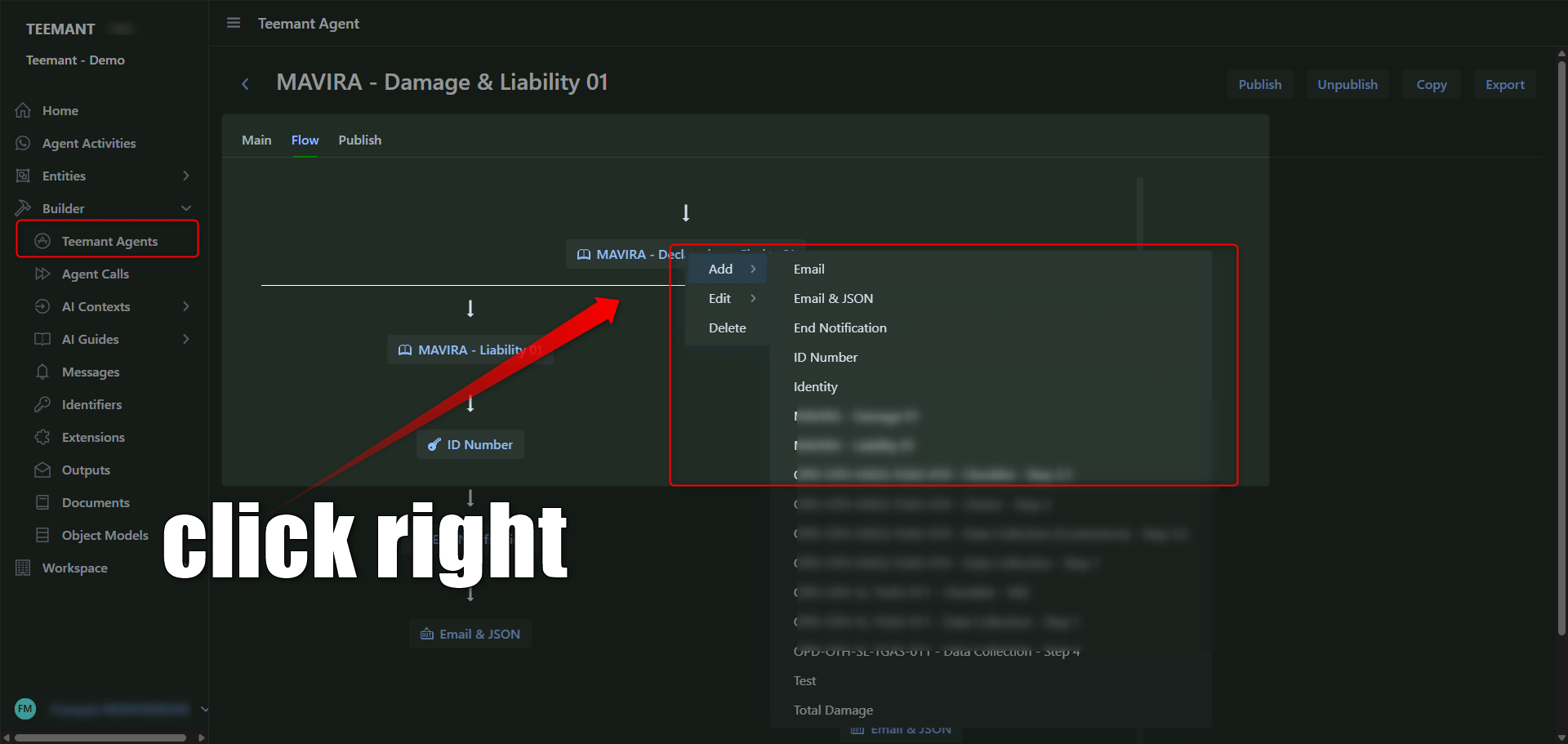
From the Builder screen:
- Right-click or click on a node to:
- Add a new guide, message, or other element.
- Edit an existing one.
- Delete a node.
Each block can have conditions attached, enabling branching based on user choices or system criteria.
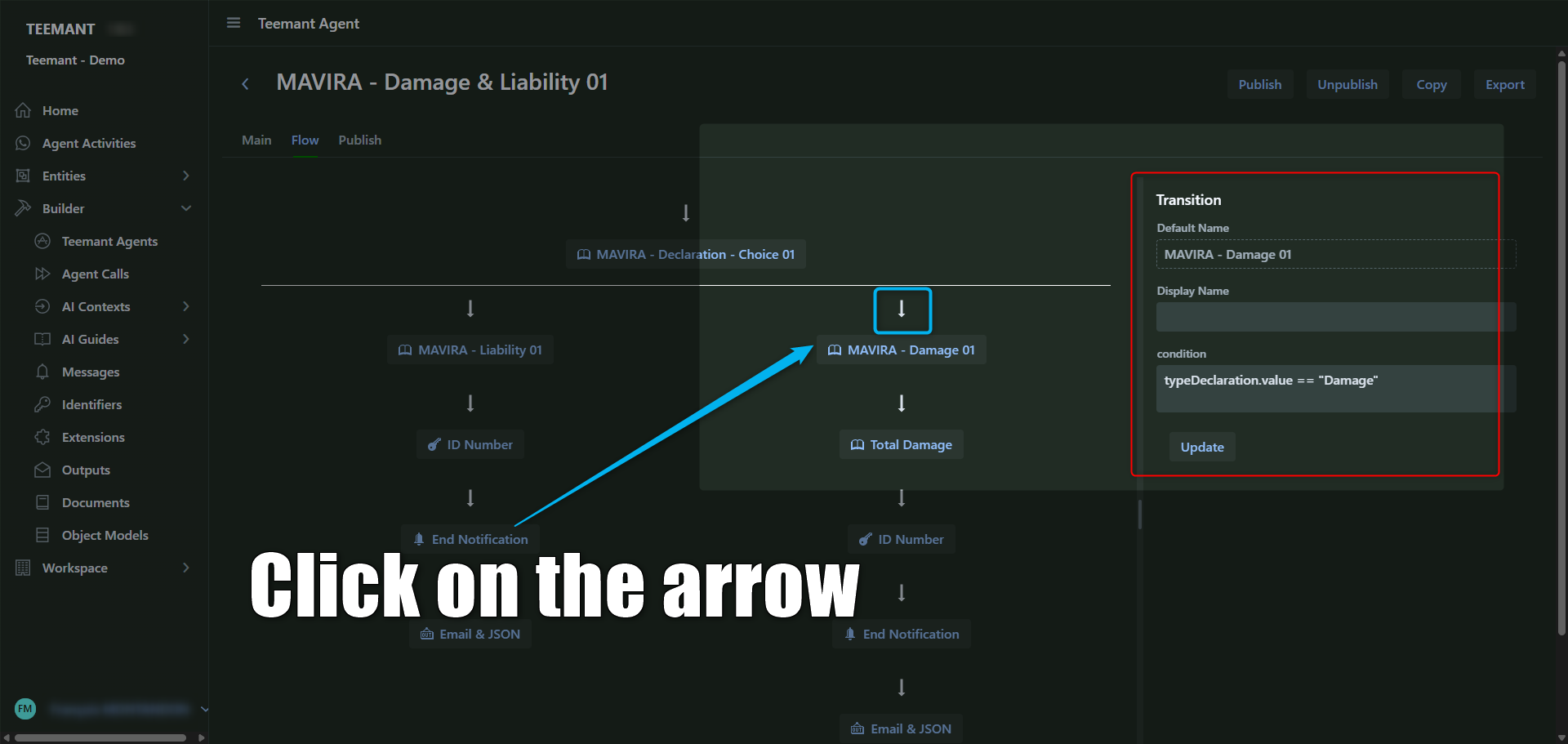
🔀 Dynamic Navigation: Routing Based on Conditions
The visual builder is structured as a tree of guides and outputs. Between each node (like a guide or message), the agent transitions based on logic defined by the designer.
To define these transitions, the designer must click on the arrow linking two steps in the flow.
📍 As shown in the screenshot:
- Click the arrow between nodes (here, between the "MAVIRA - Declaration - Choice 01" and "MAVIRA - Damage 01" guides).
- The right panel will open with the Transition settings.
- You’ll see:
- Default Name – the name of the next block.
- Display Name – optional user-facing name.
- Condition – the logic that triggers this path.
🧩 Examples of Conditions
You can use variables captured earlier (usually from Data Collection or Choice guides). For instance:
✅ Basic Text or Option Logic
typeDeclaration.value == "Damage"
This means the flow will continue along this branch only if the user selected "Damage" earlier.
✅ Boolean Values
incidentReported == TRUE
For yes/no questions, Teemant recognizes boolean-type fields.
✅ Numeric Conditions
claimAmount > 1000
Use math or comparison operators for thresholds.
🪜 Why Use Conditions?
- Branching for different scenarios (e.g., Liability vs Damage).
- Skipping unnecessary steps.
- Directing outputs (email, webhook, summary) based on user input.
- Personalized user journeys.
Agents Calls
AI Contexts
New Paragraph
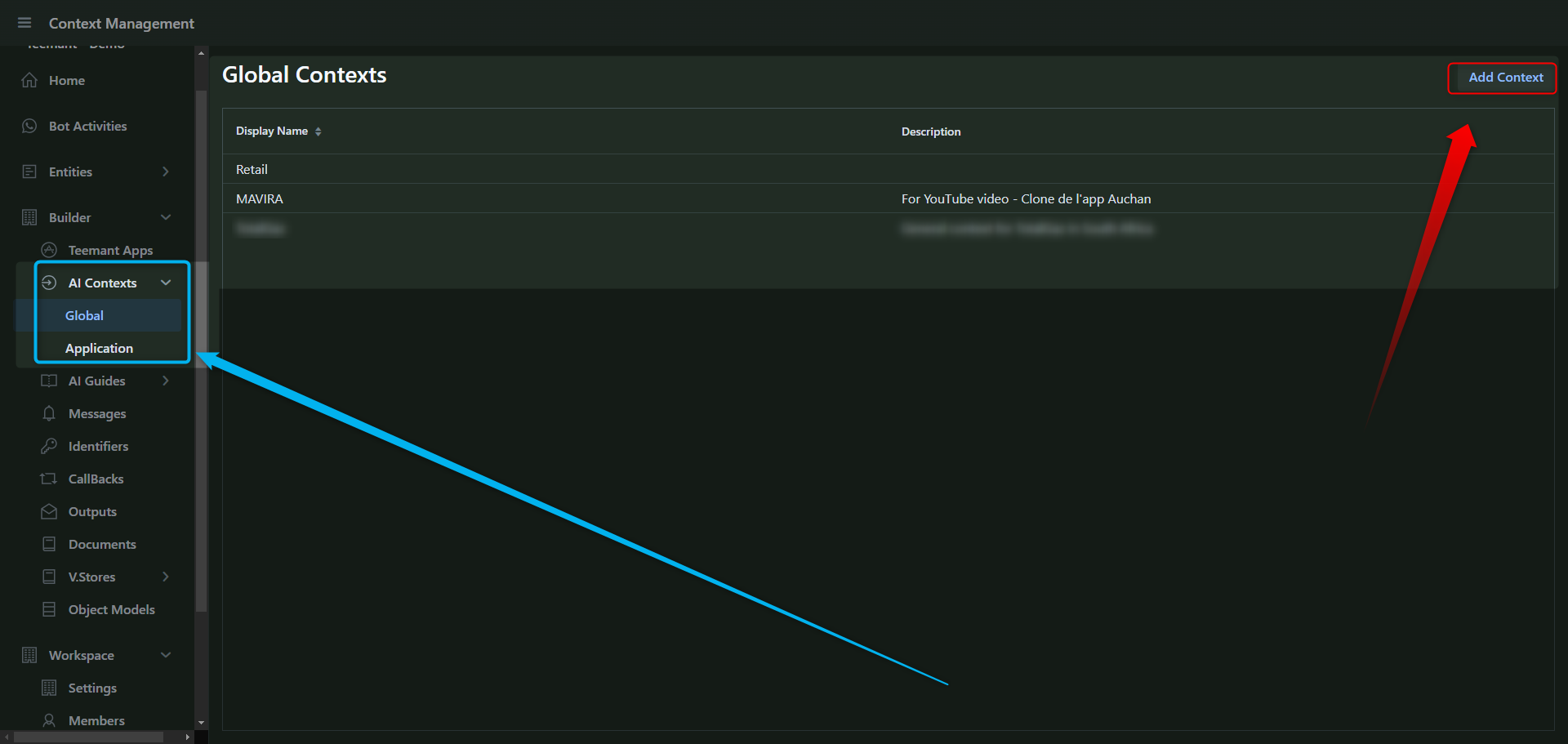
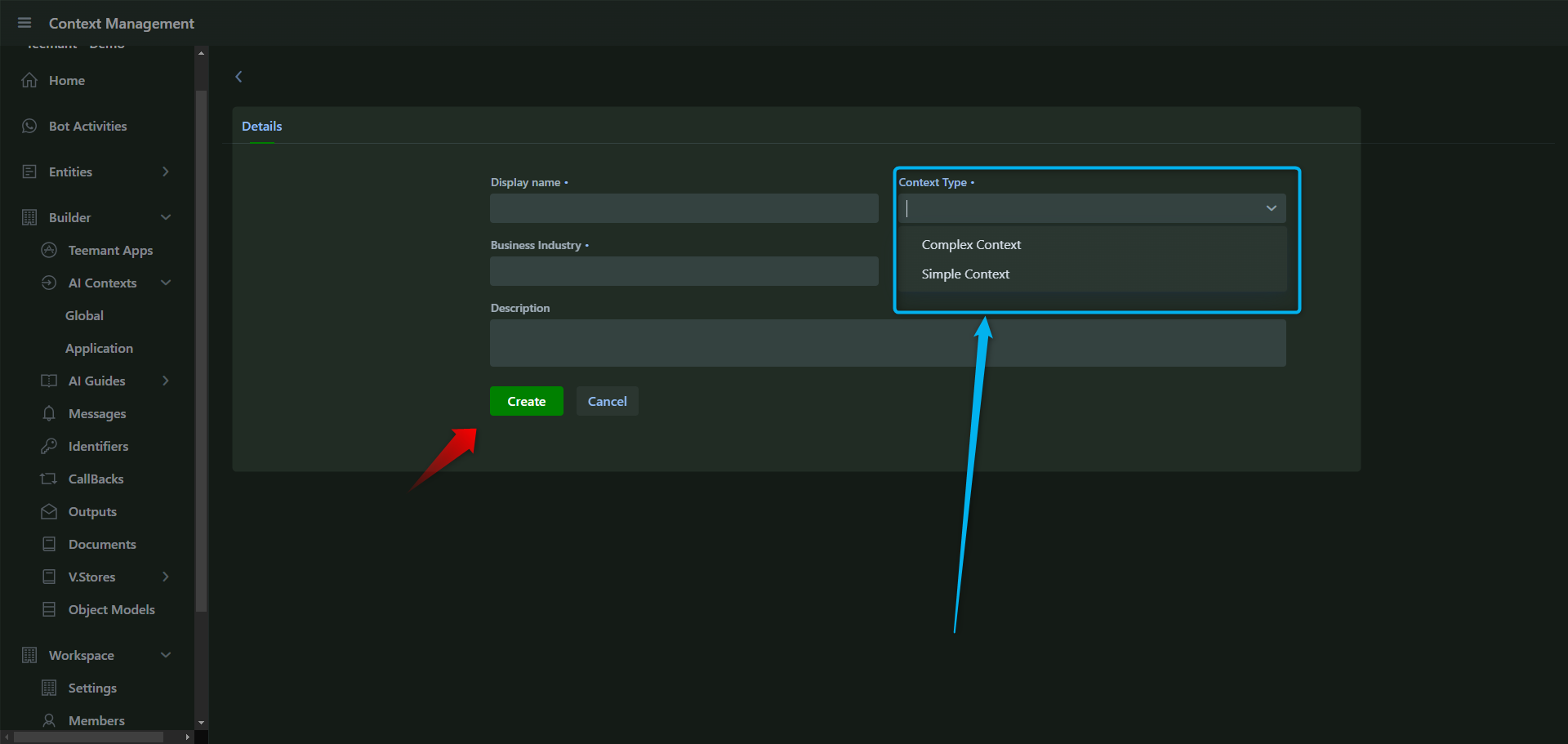
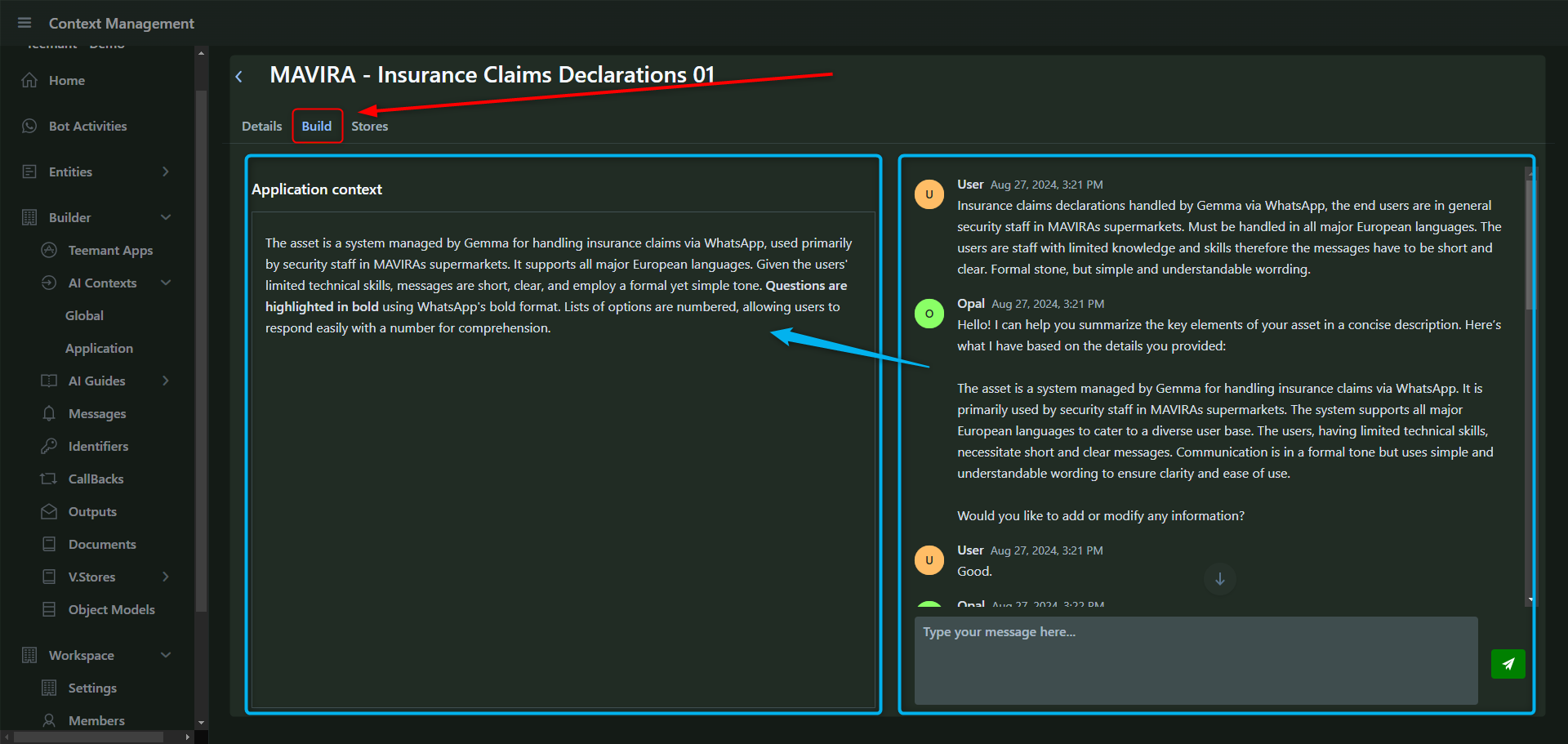
AI Guides
AI Guides in TeemantSoft serve as structured instructions for Teemant AI agents, such as Gemma, to perform specific tasks. These guides define how the AI interacts with bot users, collects data, and processes requests.
For bot designers, Flint is the AI assistant available to help build guides. You can ask Flint for guidance on how each AI Guide works and how to optimize them.
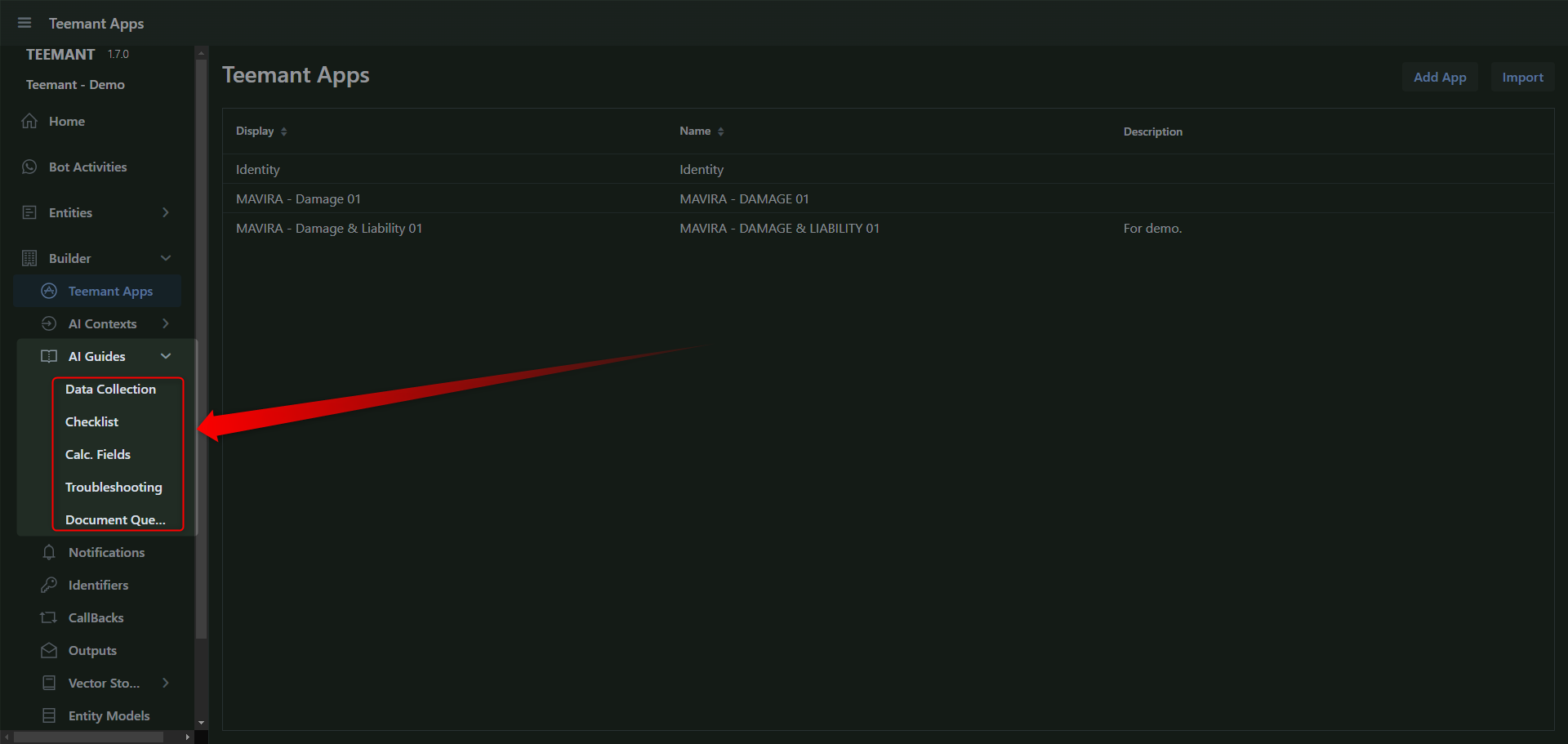
Types of AI Guides
1. Data Collection
📌 Purpose: Automates structured data collection from bot users.
- Defines the questions the AI agent should ask.
- Ensures all necessary information is gathered before proceeding.
- Can validate responses based on predefined rules.
2. Checklist
📌 Purpose: Verifies step-by-step conditions or prerequisites.
- Ensures that specific criteria are met before progressing.
- The AI agent confirms each item with the bot user.
3. Calculated Fields (Calc. Fields)
📌 Purpose: Performs real-time calculations based on user inputs.
- Uses predefined formulas to compute results dynamically.
- Helps in decision-making and automated assessments.
4. Troubleshooting
📌 Purpose: Guides bot users through problem resolution workflows.
- The AI agent asks diagnostic questions and suggests solutions.
- Helps users resolve issues without human intervention.
5. Document Query
📌 Purpose: Extracts information from documents and structured databases.
- The AI agent retrieves and presents relevant data upon request.
- Supports various document formats and knowledge bases.
Input Providers
TeemantSoft's AI agent interacts with users through multiple communication channels, ensuring accessibility and seamless automation. The main input providers are:
- WhatsApp: Enables real-time messaging, supports text, images, videos, and documents.
- Google Chat: Integrates with business workflows for structured interactions and task automation.
- Microsoft Teams (Upcoming): Supports collaboration through direct messages and team channels.
- Email: Processes structured data, attachments, and asynchronous communications.
WhatsApp serves as a primary communication channel for interacting with the AI agent. It enables real-time messaging and supports text, images, videos, and documents, making it a versatile tool for automated workflows.
WhatsApp Number Assignment
TeemantSoft provides WhatsApp numbers upon request.
- Ideally, each workspace should have a dedicated WhatsApp number for clear separation.
- However, a single WhatsApp number can be used across multiple workspaces.
- In this case, when a bot user connects, they will be prompted to choose their workspace before proceeding.
- This setup ensures flexibility, allowing organizations to structure their communication efficiently while maintaining distinct user environments within a shared number.
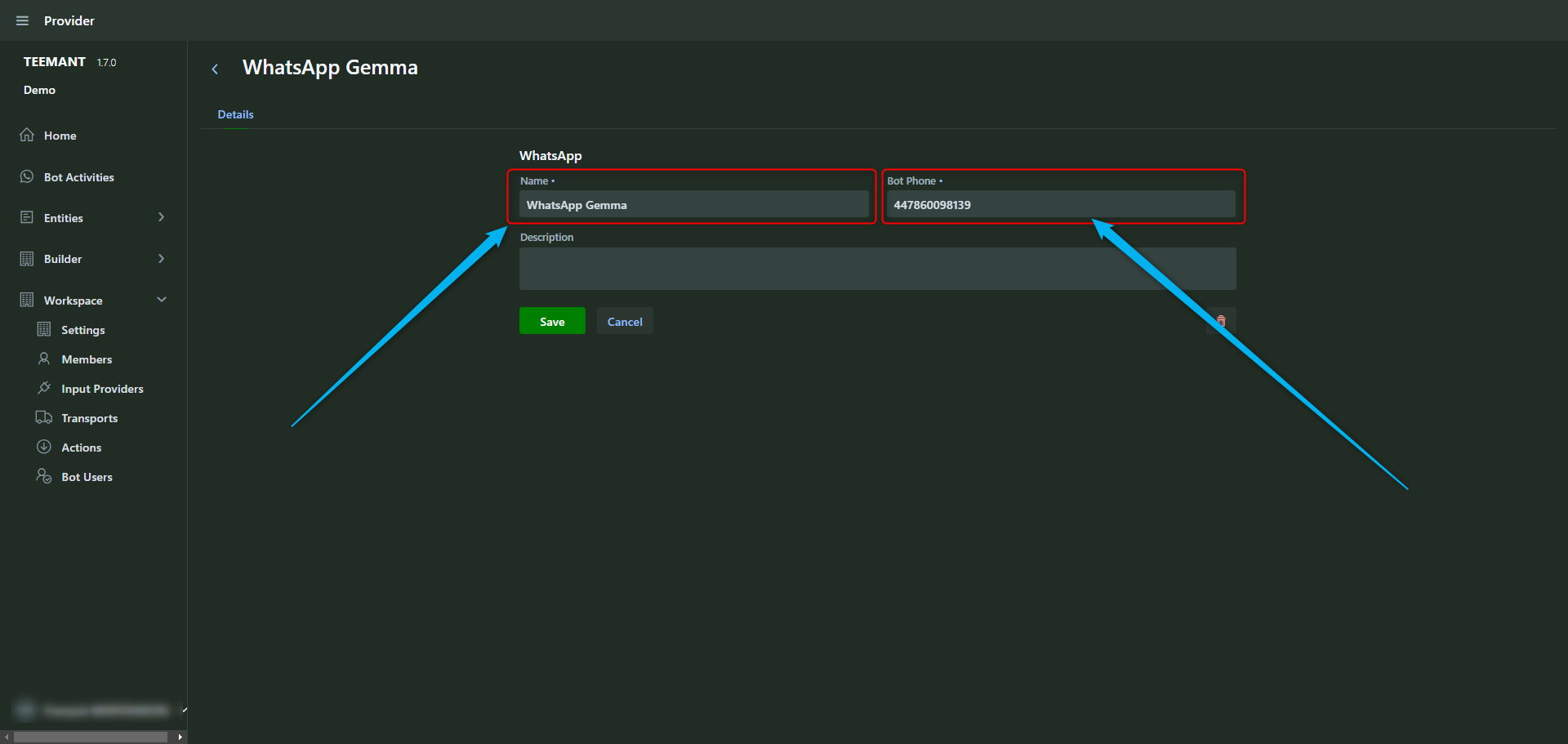
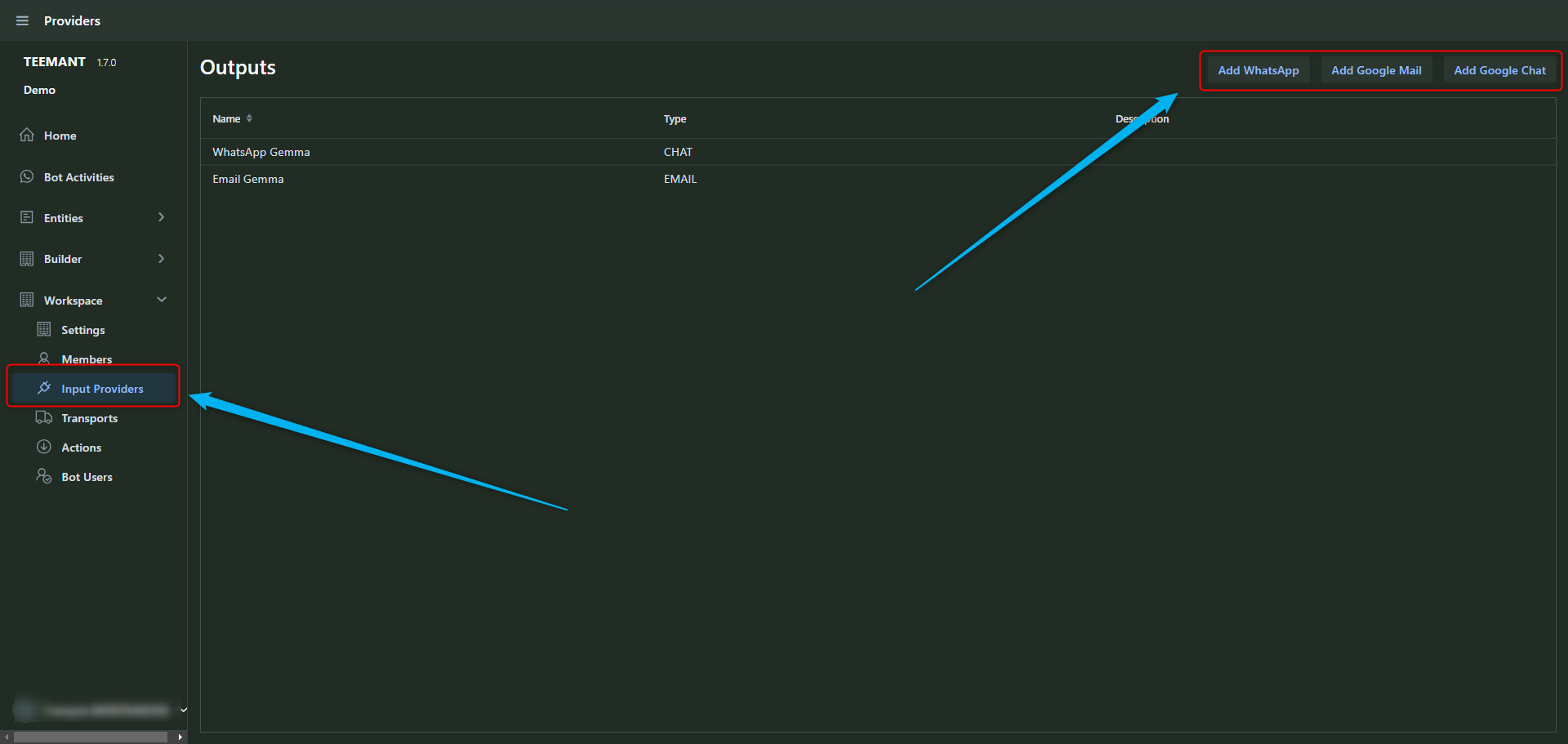
WhatsApp Setup Best Practices
To enable interactions via WhatsApp, each workspace must have an assigned WhatsApp number.
Number Assignment & Naming Convention
- Each workspace must add and configure a WhatsApp number along with a name.
- Best practice: Use the format "Input Provider Name + AI Agent Name" (e.g., WhatsApp Gemma).
- Once set up, all bot users in the workspace can interact with the AI agent through WhatsApp.
Bot User Access & QR Code Recommendation
- Instead of sharing the WhatsApp number directly, it is advised to provide the QR code.
- This ensures a smoother onboarding experience and avoids manual entry errors.
- The QR code allows bot users to connect instantly and start their interaction with the AI agent.
This structured approach ensures clarity, scalability, and ease of access for users.
Google Chat Integration
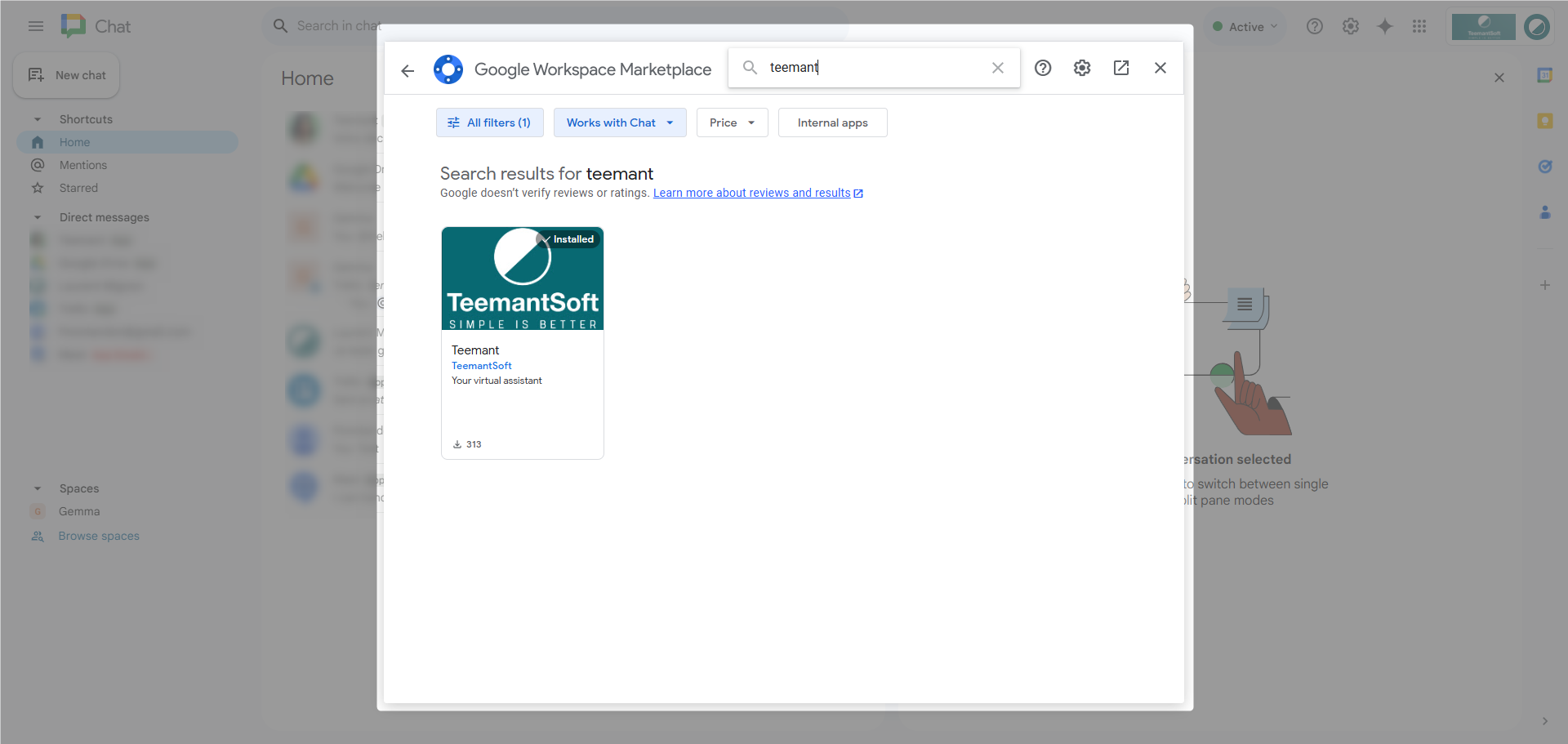
Google Chat serves as a key input provider for TeemantSoft, enabling users to interact with the AI agent within their organization's Google ecosystem.
Installation & Authentication
- Google Chat integration is based on Google authentication.
- Users must go to the Google Chat Marketplace and locate the Teemant application.
- The installation can be done via Admin Install, allowing deployment across the entire organization or selected users.
- Once installed, the AI agent will appear in the user's Google Chat contact list for direct interaction.
Access Requirements
- Only users with administration rights in Teemant can install the application.
- After installation, authorized users within the organization can seamlessly communicate with the AI agent.
- This setup ensures secure and scalable integration within enterprise environments, leveraging Google’s authentication framework.
For a step-by-step installation guide, refer to our detailed Google Chat Installation Presentation.
This setup ensures secure and scalable integration within enterprise environments, leveraging Google’s authentication framework.
Microsoft Teams Integration
Soon, TeemantSoft will support Teams integration, enabling seamless AI-powered interactions within enterprise collaboration environments.
Email Integration
A future update will introduce email-based interactions, allowing structured workflows through automated email processing.
The Teemant Workspace
A workspace in TeemantSoft functions as an isolated environment, similar to a tenant, where different organizations, departments, or projects can operate independently while sharing the same platform.
Key Features of a Workspace
- User Management: Each workspace has its own administrators and bot users.
- Input Providers: Dedicated configurations for WhatsApp, Google Chat, Microsoft Teams, Email, and future integrations.
- AI Engine & API Key: Each workspace requires its own AI engine, which necessitates a distinct API key.
- Teemant Apps Access: Users within a workspace can access and interact with all Teemant Apps designed and/or published in that environment.
- AI Agent Interaction: When a bot user contacts the AI agent, they can choose from the different Teemant Apps available to them.
This structure ensures data isolation, customization, and efficient access control, making it ideal for businesses that require multi-environment AI automation.
Workspace Creation
Step 1: Adding a New Workspace
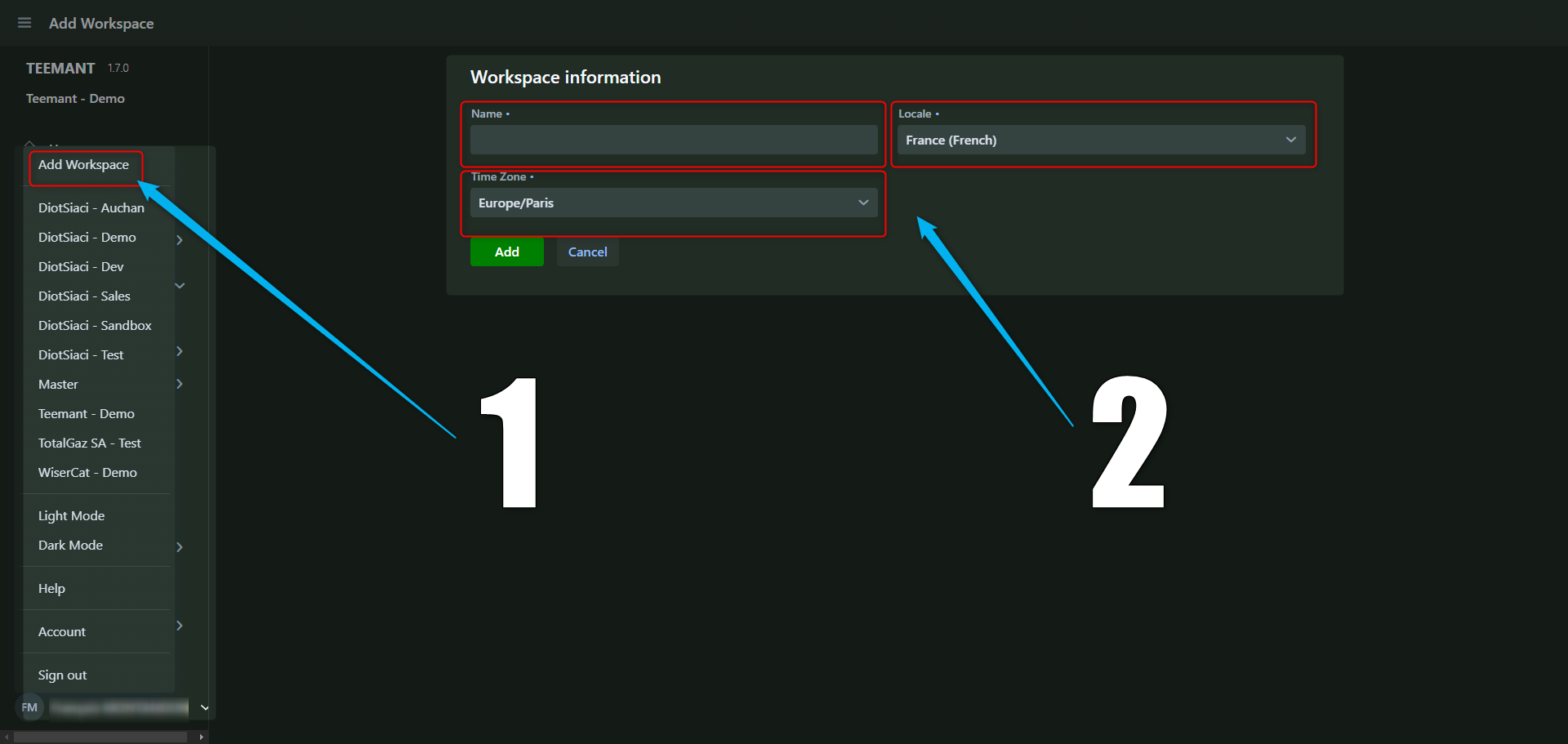
📌 Navigate to the workspace settings
- On the left-hand menu, click on your name.
- Click “Add Workspace” in the workspace list.
- Enter the workspace name, select the appropriate time zone, and define the locale (e.g., France - French).
- Click “Add” to create the workspace.
🛠️ Tip: Choose a workspace name that reflects the project or team using it.
Step 2: Configuring the Main Settings
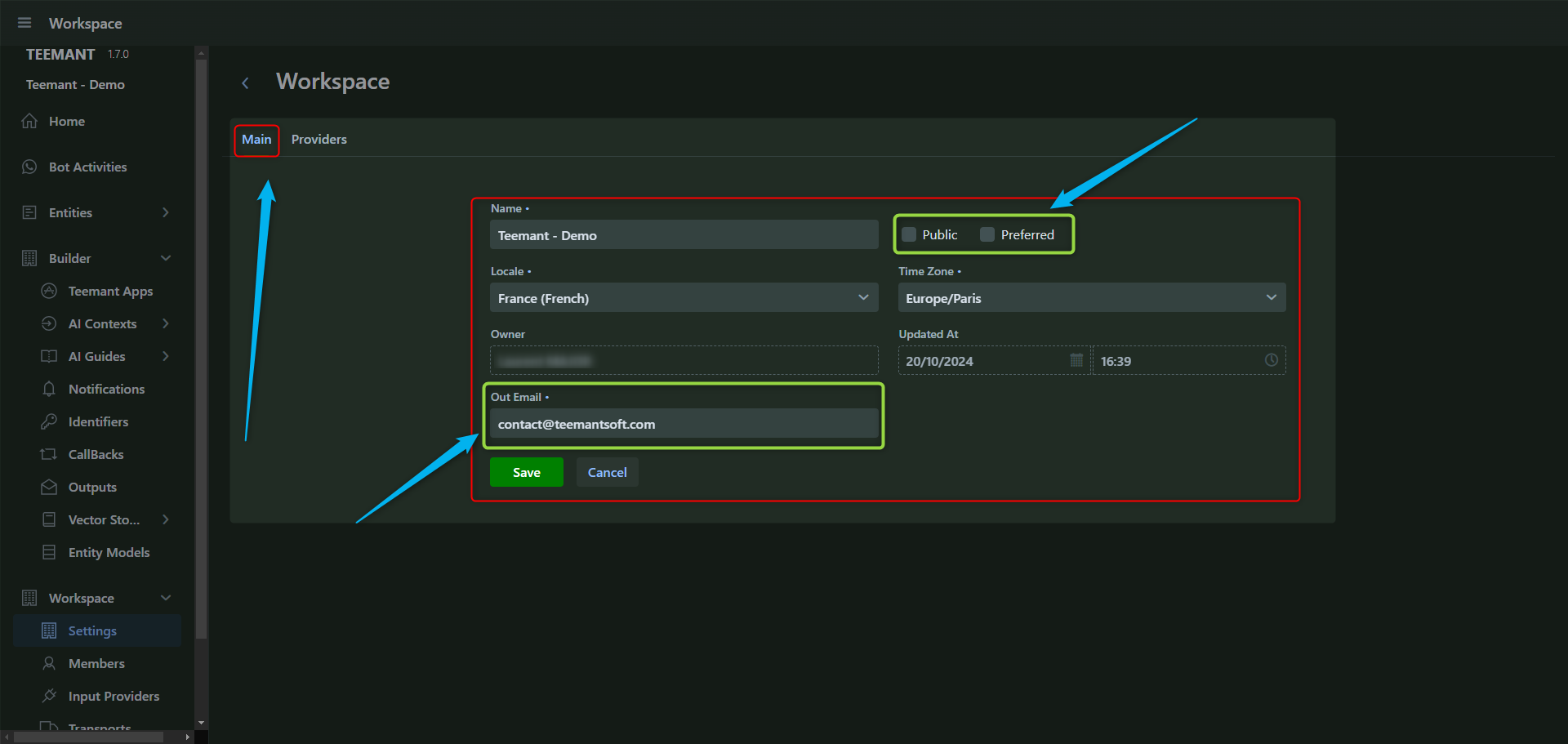
📌 Defining core workspace attributes
In the Main tab, enter
- Workspace Name: This should match the intended use of the workspace.
- Locale: Defines language preferences.
- Owner: Assign a workspace administrator.
- Outgoing Email: Set the email for system notifications.
- Public/Preferred settings: Adjust visibility and preference options.
- Click “Save” to apply the settings.
🛠️ Tip: The Public setting makes the workspace accessible to any bot user who interacts with the AI agent, while Preferred prioritizes it in the workspace list.
Step 3: Configuring AI Engine
Each workspace in TeemantSoft requires an AI engine API key to function. Currently, TeemantSoft integrates OpenAI as the primary AI engine, with future support for Llama and Mistral in development.
Current Process for API Key Management
- API keys are available upon request and must be manually added in the Providers tab of each workspace.
- Each workspace requires a unique API key to ensure data isolation and control.
- Administrators are responsible for securing and managing these API keys.
Future Enhancements
Automated API Key Generation: In later stages, users will be able to generate and assign API keys directly from the platform.
- Multi-AI Engine Support: TeemantSoft will integrate additional AI engines, including Llama and Mistral, allowing users to select the best AI model for their needs.
- Dynamic AI Engine Switching: Workspaces will be able to configure and switch between different AI engines seamlessly.
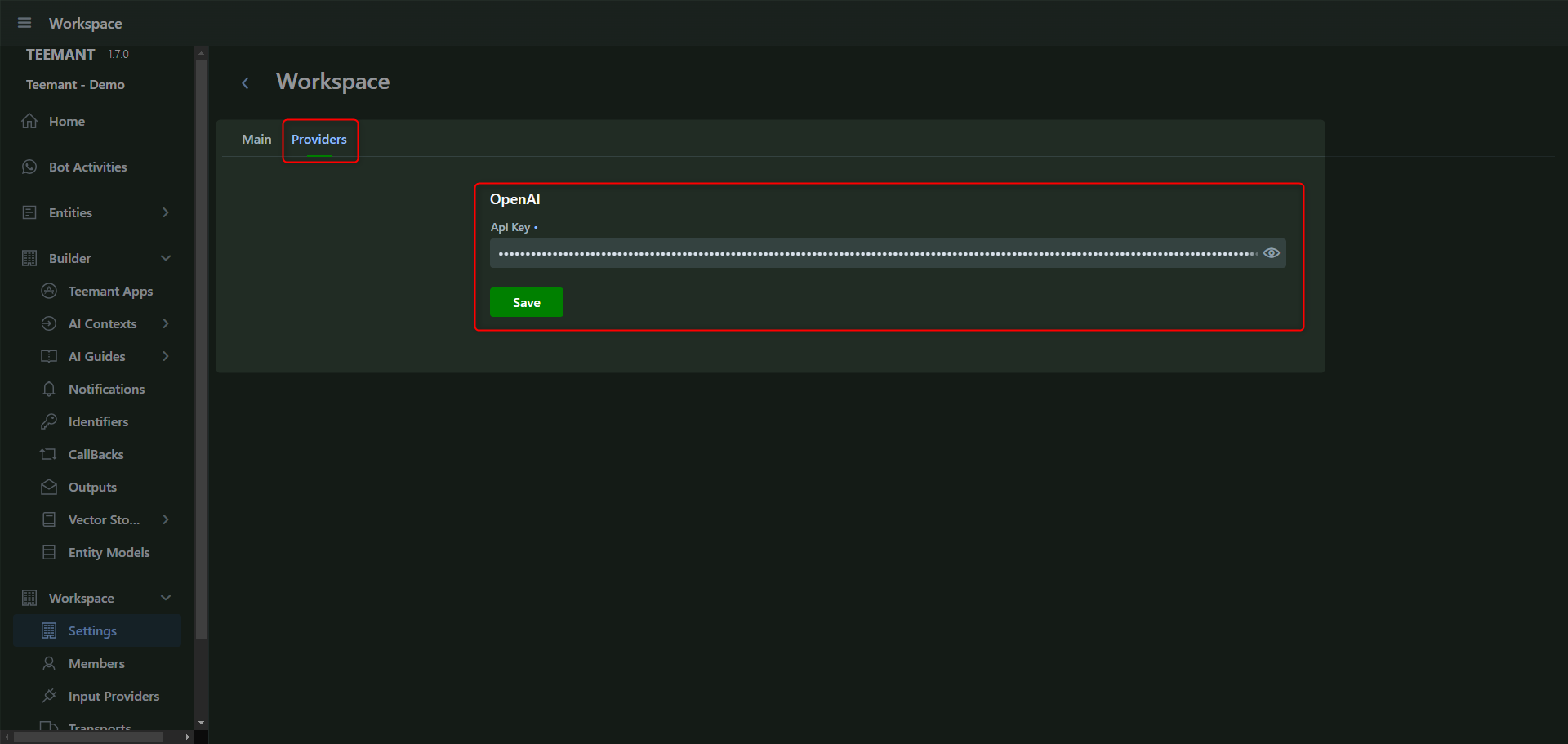
📌 Setting up communication channels and AI processing
- Navigate to the Providers tab.
- Add the required API key for the AI engine (e.g., OpenAI).
- Click “Save” to confirm the configuration.
🛠️ Tip: Each workspace requires a distinct API key to ensure data isolation and security.
Best Practices for Workspace Management in TeemantSoft
When developing Teemant Apps, it is recommended to create three distinct workspaces to ensure a structured development process and smooth deployment.
1. Project Dev (Development Workspace)
- Used by bot designers to develop Teemant Apps based on flowcharts, forms, and text inputs.
- AI guides are set up, refined, and tested within this controlled environment.
- Once an app is ready, it is published and prepared for further testing.
2. Project Test (Testing Workspace)
- Apps are published here for validation.
- Test users interact with the AI agent and provide feedback on performance and usability.
- Any bugs or inconsistencies are addressed before moving to production.
3. Project Prod (Production Workspace)
- The final deployment space where fully tested and validated apps are published.
- Bot users interact with the AI agent in a live environment.
- Ensures that only stable and optimized applications reach end users.
Final Check
✔️ Correctly Configured Workspaces: Ensure each workspace is named appropriately, localized, and has the correct administrators assigned.
✔️ Input Providers Setup: WhatsApp, Google Chat, Microsoft Teams, and Email should be properly linked.
✔️ AI Engine API Key: Each workspace should have a distinct API key to ensure data isolation.
✔️ Access Control: Only authorized users should have admin rights for security and controlled testing.
By following this structured approach, organizations can maintain a clear development cycle, reduce errors, and deliver high-quality AI-driven automation. 🚀
User Management
TeemantSoft organizes user access into two main categories: backend users who manage the workspace and bot users who interact with AI agents through external communication platforms. This structured approach ensures clear role distribution, security, and controlled access to TeemantSoft functionalities.
Members or Backend Users (Admin Panel Access)
Members have access to the TeemantSoft platform to manage workspaces, users, and application deployment.
- Navigate to Workspace → Members in the left-hand menu.
- Click “Add Member” to create a new user or select an existing user to modify their roles.
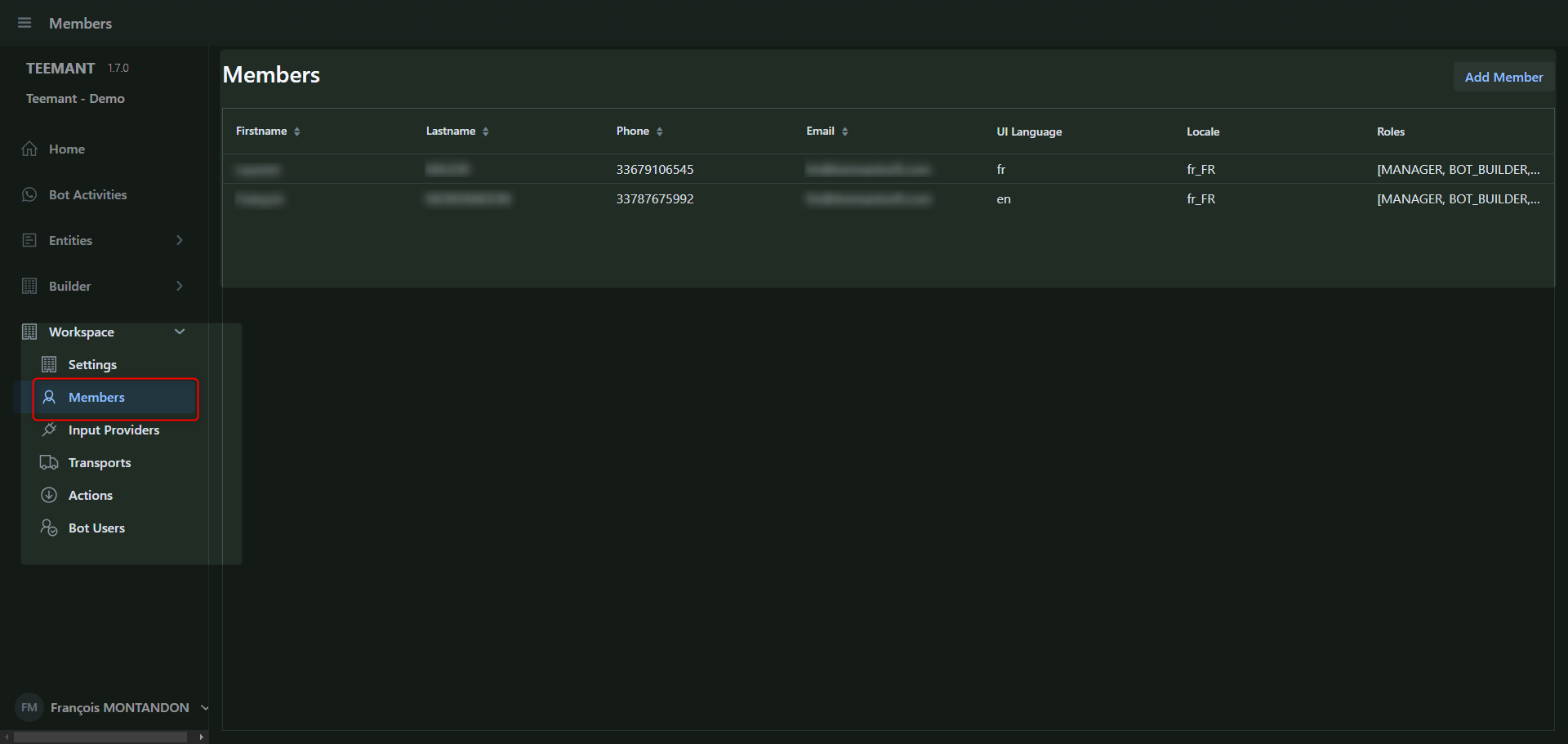
Entering User Information
Fill in the required fields:
- Email (Account): The user's login email.
- First Name & Last Name: Identifies the user within the system.
- Phone Number (optional but recommended).
- UI Language: Choose the interface language (e.g., English, French).
- Locale: Select the regional settings for the user.
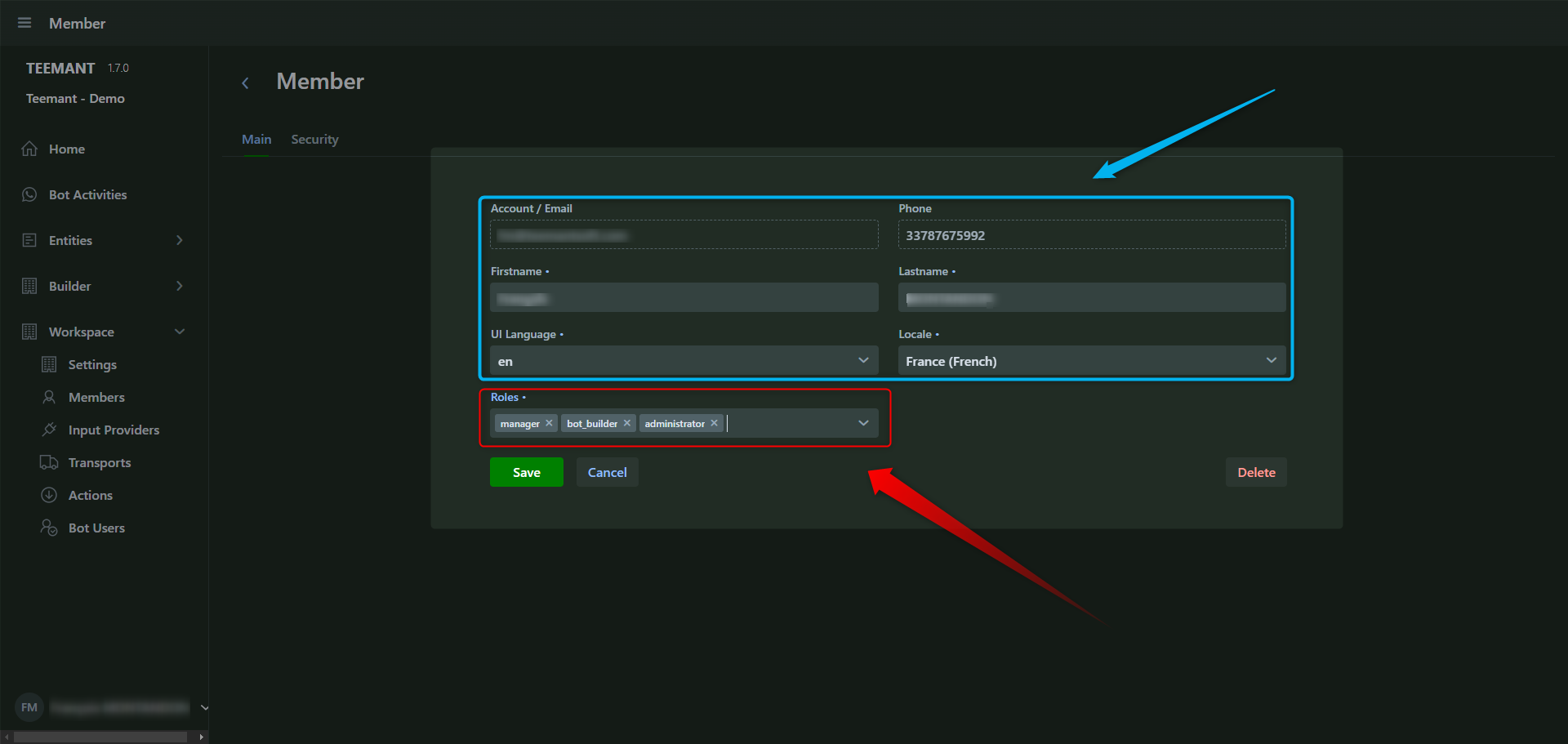
Assigning User Roles
- In the Roles section, select the appropriate roles for the user.
- A user can have one or multiple roles depending on their responsibilities.
Saving Changes
- Click “Save” to apply the new settings.
- If you want to cancel changes, click “Cancel” before saving.
- To remove a user, click “Delete” and confirm the action.
These steps ensure that each team member has the correct permissions to manage and operate within the TeemantSoft platform. 🚀
Administrator
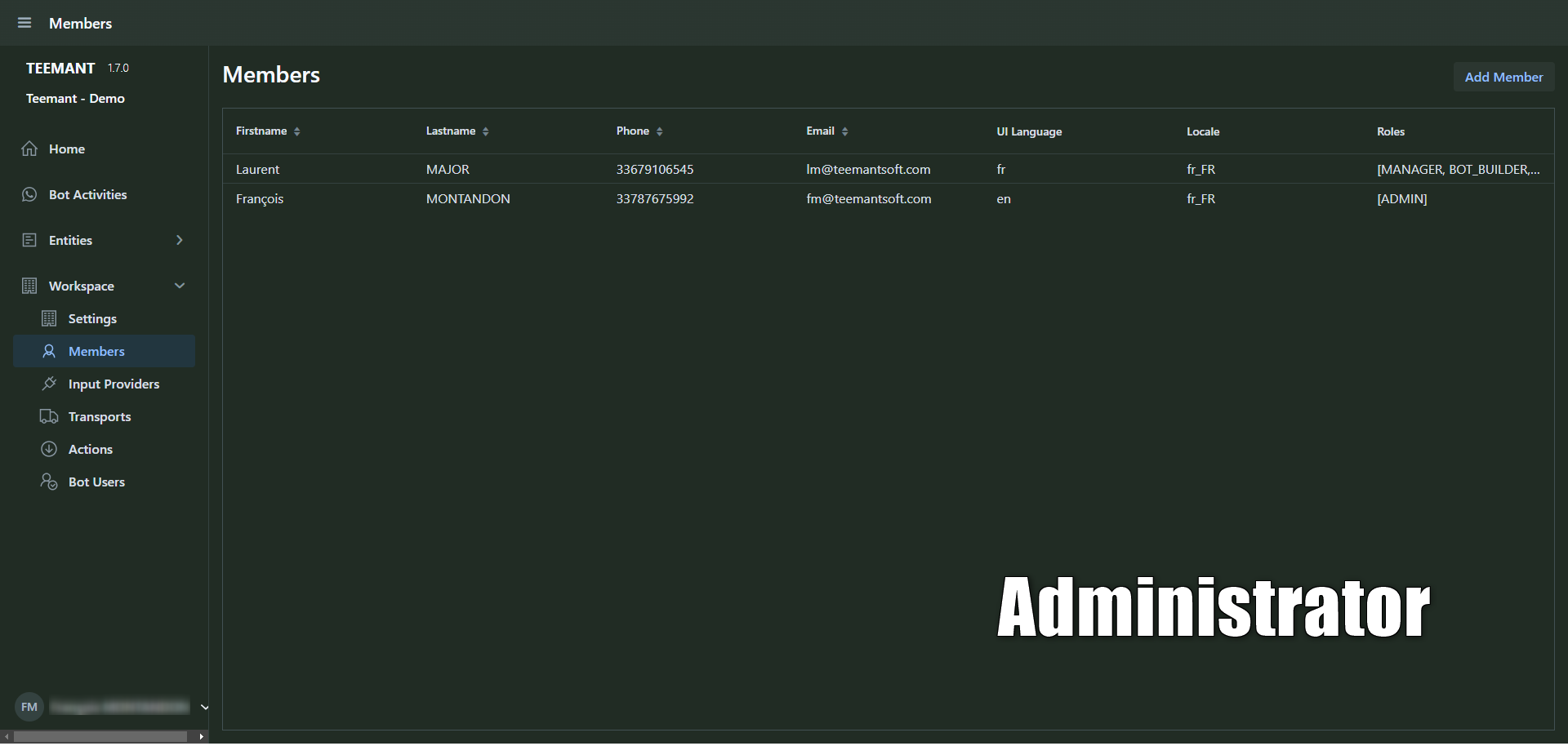
- Has full control over workspace management, including user administration, workspace settings, and system configurations.
- Does not have access to AI configurations or app development.
Manager
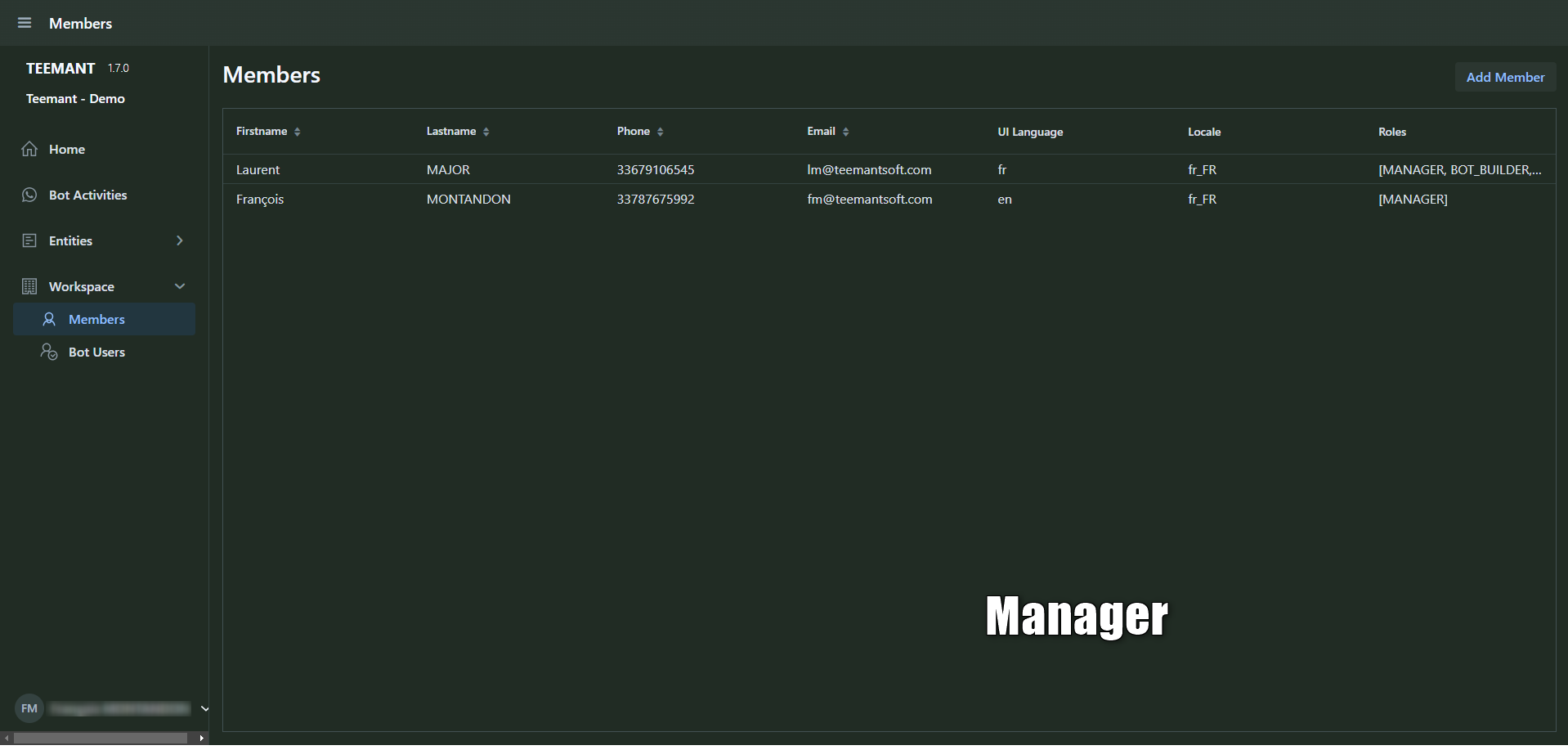
- Oversees workspace operations, manages bot users, team members, and Teemant App deployment.
- Can modify workspace settings and supervise interactions but cannot access core AI development tools.
Bot designer

- Responsible for creating, configuring, and optimizing Teemant Apps within a workspace.
- Can design AI workflows, guides, and automation sequences but does not manage overall workspace settings.
Bot Users (AI Interaction via External Platforms)
Bot users interact with Teemant AI agents via WhatsApp, Google Chat, Microsoft Teams, and other communication tools.
Their access depends on the workspace settings:
- If the workspace is public, any user can access the AI-managed apps without registration.
- If the workspace is private, only registered users will be able to interact with the AI agent.
This distinction between backend users and bot users allows organizations to securely manage AI interactions while maintaining structured control over workspace operations. 🚀
Publishing, Copying, and Exporting an Application
TeemantSoft allows users to publish, copy, and export applications, ensuring seamless deployment and transfer across different workspaces. These features provide flexibility in managing applications throughout their lifecycle.
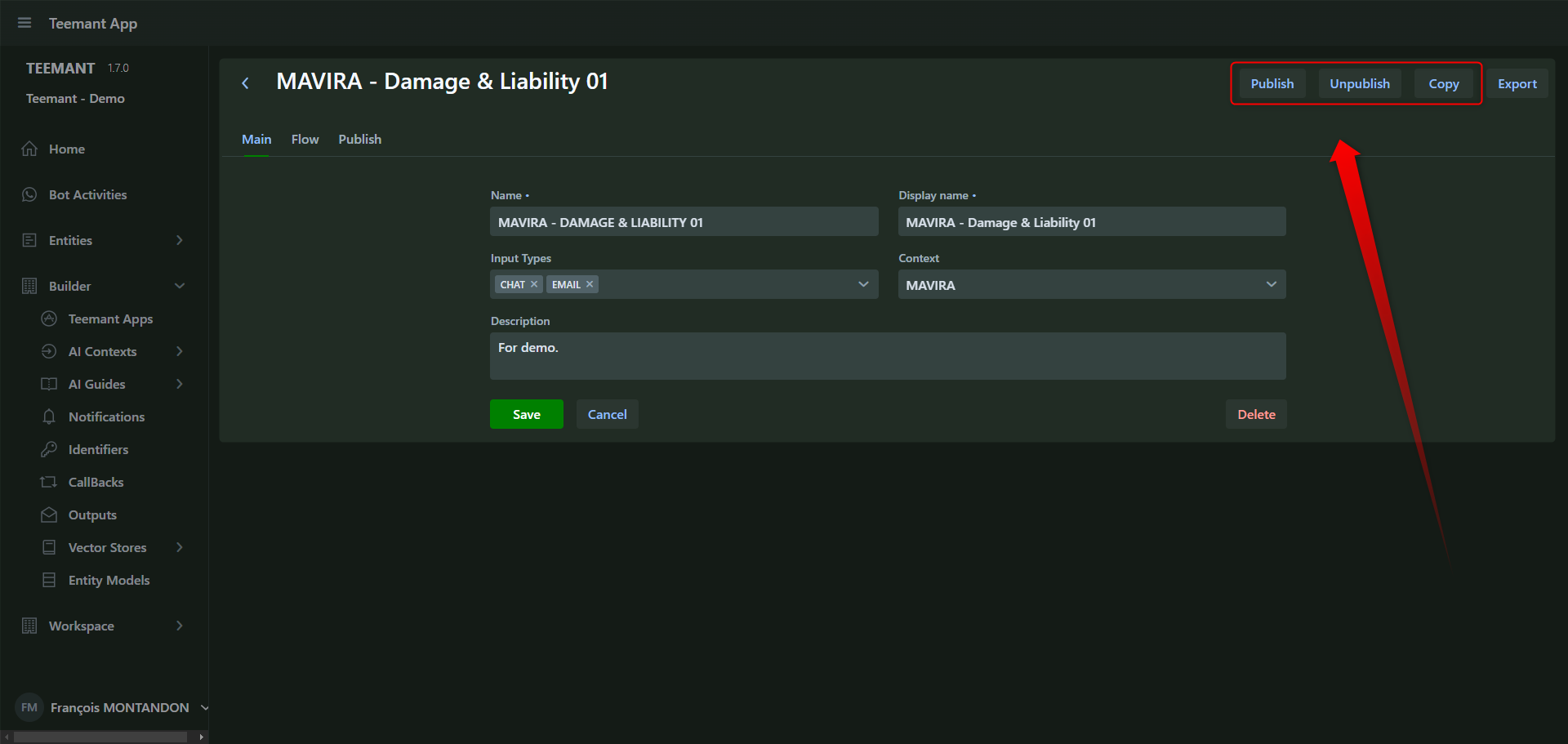
Publishing an Application
Publishing an application makes it available for use by a Teemant AI agent. Once published, the AI agent can execute the app when a bot user initiates a conversation via WhatsApp, Google Chat, Microsoft Teams, or other integrated platforms.
Steps to Publish an Application
- Open the Teemant App you want to publish.
- Click on the "Publish" button (top-right corner).
- Select the target workspace from the dropdown list.
- Confirm the selection to deploy the app to the chosen workspace.
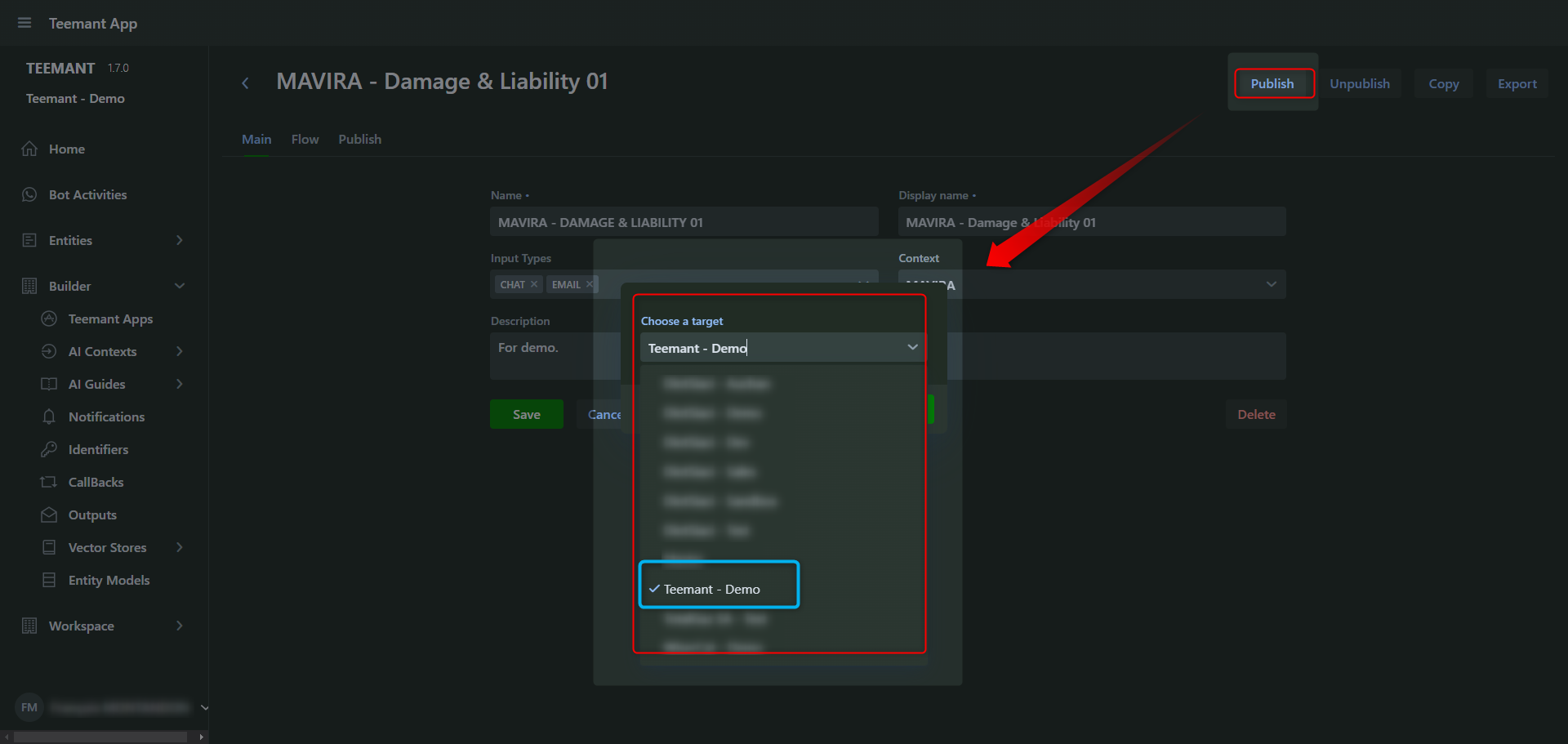
📌 Best Practice:
- The master workspace is generally the development environment ("Company Name - Dev").
- After validation, the app is published in the test workspace ("Company Name - Test").
- Once fully approved, it is finally deployed in the production workspace ("Company Name - Prod"), where real bot users can access it.
Unpublishing an Application
- If an application needs updates or is no longer required, you can unpublish it.
- Click the
"Unpublish" button to
remove the app from active use.
Copying an Application
Copying an application allows you to duplicate an app within the same workspace or modify it without affecting the original version.
When to Use Copying?
- To create an alternate version of an app with different configurations.
- To deploy a similar app in multiple workspaces for different user groups.
Exporting an Application
Exporting an application generates a .tee file, which can be imported into another workspace, even on a different domain.
Steps to Export an Application
- Open the Teemant App you want to export.
- Click "Export" (top-right corner).
- The system generates a .tee file for download.
This file can later be imported into another workspace.
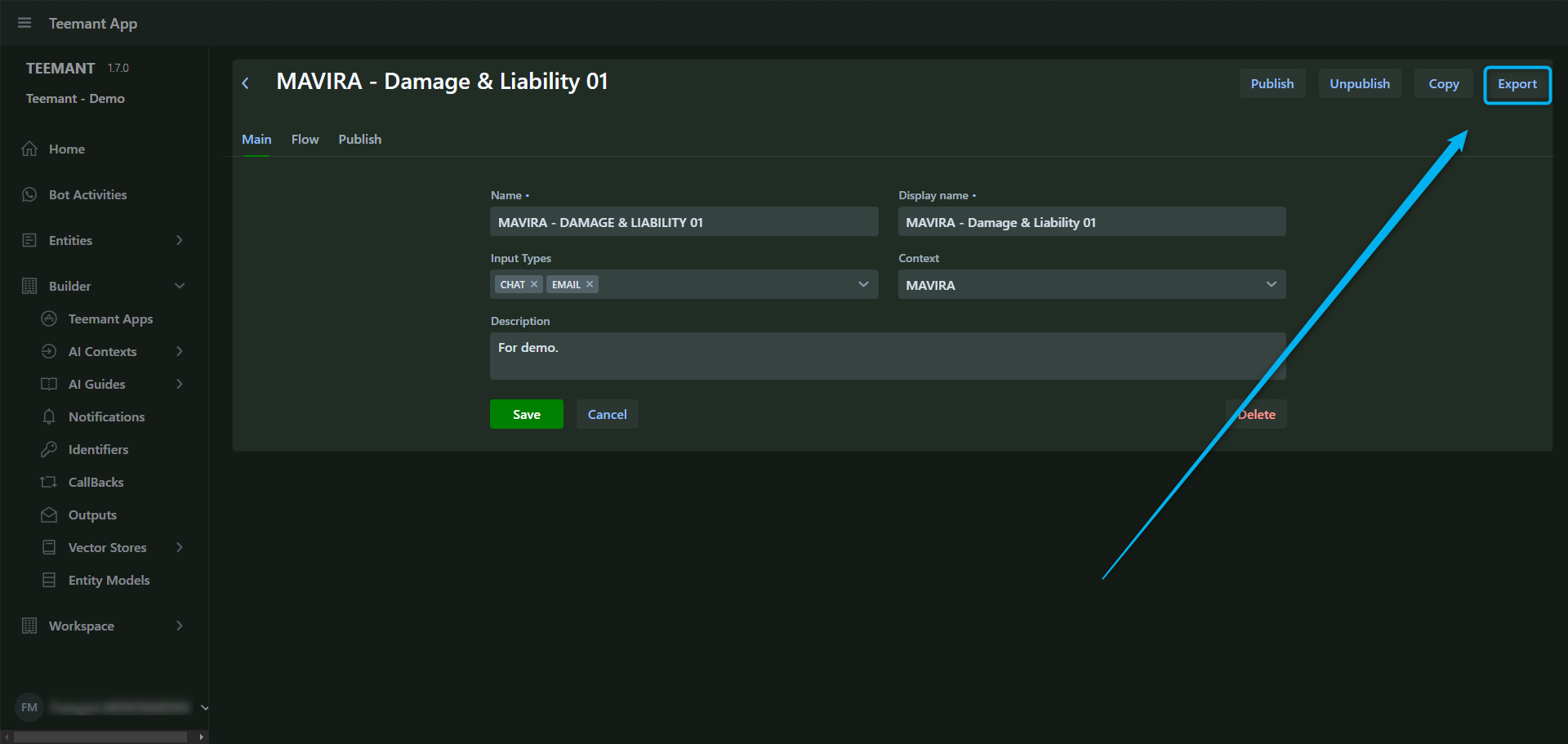
When to Use Exporting?
- If a customer has separate domains for development, testing, and production.
- When moving an application between entirely different Teemant instances.
- To create backups before major modifications.
Teemant Demo
Some users, including customers and resellers, are granted access to the TeemantSoft demo platform at demo.teemant.ai for testing and exploration purposes.
They can interact with the AI agent via WhatsApp using the dedicated test number: +44 7860 098139 (TeemantSoft Test) or use the following QR code.

Alternatively, they can use their Google Chat account and install the Teemant application following the standard setup process.







